Force and Motion Worksheets (Definition and Examples)
Grade 6 Science Worksheets

Force and motion are core concepts in physics. Force is the push or pull on an object, while motion is the resulting change in its position over time. Forces cause objects to move, accelerate, or change direction. Understanding force and motion is essential for studying the mechanics of the physical world.
What Is Force?
You push a cart or squeeze a piece of clay. You pedal a bicycle or kick a football. In all these actions you are applying force. Force is something that changes the motion or shape of an object. Newton’s first law of motion states that every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force to change its motion. The examples mentioned are all Mechanical Forces, where one object touches another. There are many other types of forces – electricity, gravitation, and magnetism which act without contact among objects. For now, we will focus only on mechanical forces. You can also download the 6th Grade science worksheets .
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
What is Motion?
Motion is when an object changes its location in space. Motion is relative to another object rather than absolute.
If you are sitting in a moving train, a person on the platform sees you in motion. However, the person sitting next to you in the same train sees you perfectly still. Motion is determined by the difference between the positions of the two objects or observers.
Similarly, if you are in a moving car and there’s another car alongside, moving slightly faster than yours, you see a very small difference in motion with respect to your car or your position. Yet, both cars would appear as moving very fast to a stationary observer.
Every motion is in relation to some other place or object in the Universe – it is with respect to a Frame of Reference. Every motion is an Apparent Motion with respect to that frame of reference.
Important formulas in the chapter force and laws of motion.


Force and Motion are related
What is Force? An object at rest can only be put into motion by a cause. When you push a stationary cart, it starts to move. This cause is the force you’ve applied. Force can cause an object to move, it can cause an object to change direction, and it can cause an object to slow down and stop.
When you hit a ball coming towards you, you are applying force to change the direction of that ball. When you roll a ball on a rough carpet, it eventually slows down because Friction (a kind of force) between the carpet and the ball slows the ball down.
There cannot be moved without force. And, a force always causes motion or a change in motion and for years physicists have sought to show that the four basic forces are simply different manifestations of the same fundamental force.
eTutorWorld Understands Math Tutoring | Online Math Worksheets are Important Tools
Understanding graphs, charts, and opinion polls in a newspaper, for calculating house and car payments, and for choosing a long-distance telephone service are impossible without strong math skills …and the only way to develop strong math skills is by constant practice.
‘Practice makes a man perfect’ holds true for no other field better than for math. A middle or high school student must set aside a minimum of an hour for math every day. Other than textbooks, worksheets help you revise and understand concepts better.
Our expert tutors prepare online maths worksheets that are age and grade-appropriate. Grade-wise math worksheets for Elementary Math, Arithmetic, Pre-Algebra, Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Statistics, Pre-Calculus and Calculus can be solved to improve math skills, to get ahead or to even catch up.
You may download these FREE online math worksheets in the PDF format, and then print and email us their solutions for a free evaluation and analysis by eTutorworld’smath expert tutors.
You may solve these worksheets by yourself or with your peers while studying together.
The Answer Key at the end of each worksheet allows for a self-evaluation.
Personalized Online Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12, Test Prep help for Standardized tests like SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE and AP. You may schedule online tutoring lessons at your personal scheduled times, all with a Money-Back Guarantee. The first one-on-one online tutoring lesson is always FREE, no purchase obligation, no credit card required.
For answers/solutions to any question or to learn concepts, take a FREE CLASS.
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just book a free class to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
What is Speed?
Speed is how we measure motion. It is a function of time and distance – how far an object has moved in a period of time. It is the ratio of distance over time. A car that has traveled 60 kilometers in one hour implies that its speed is 60 kilometers per hour.
In reality, the car would have moved at different speeds over the hour. It would have started from rest (zero speed) and then gradually increased its speed over the hour so as to cover 60 kilometers. Hence, speed is often referred to as Average Speed.
Speed (or Average Speed) = Distance/Time
What is Velocity?
Speed does not indicate the direction of motion. When we include direction in the motion of an object, then we are referring to the Velocity of the object. For example, an object that is moving south at 60 kilometers per hour, indicates its velocity – it has magnitude (speed) as well as direction (south). Velocity is the Displacement of an object rather than the distance traveled. It is a displacement per time ratio in a particular direction.
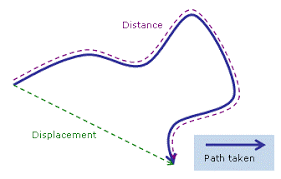
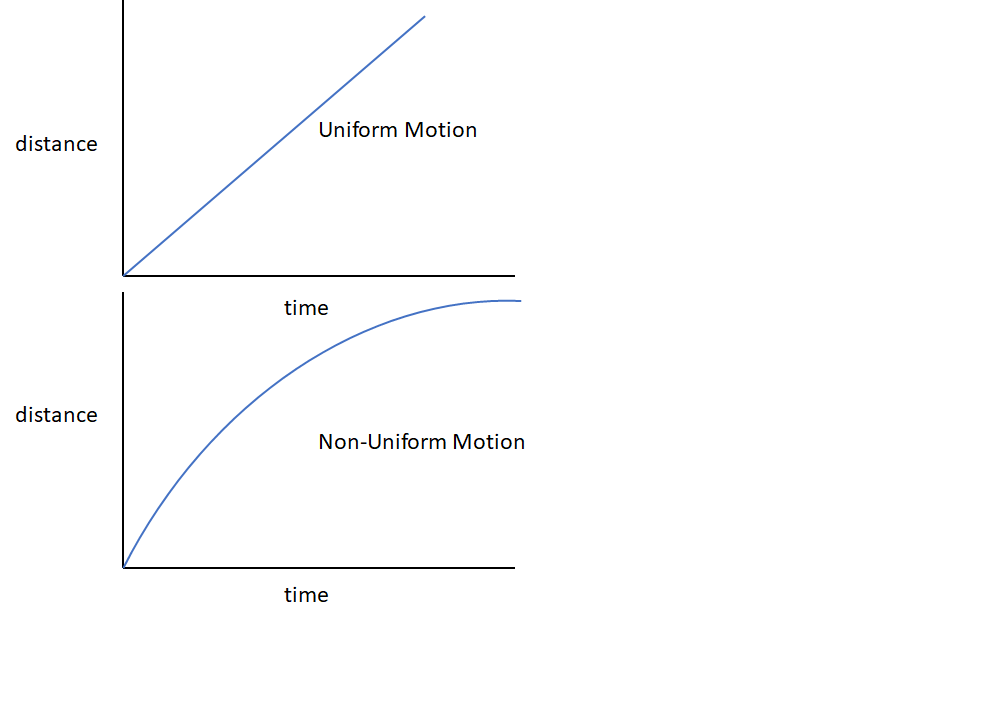
What is Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion?
When both the speed and direction of a moving object are constant, the motion of the object is said to be Uniform – it covers equal distance in equal intervals of time.
A car that covers 30 meters in every second is said to have a uniform speed of 30 meters per second.
An object that covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time is said to have Non-uniform motion. A horse that runs a race at different speeds at different points of time would be a good example.
What are Acceleration and Deceleration?
If the velocity of an object changes (increases) from one time period to another, the object is undergoing an Acceleration. Or, if the velocity decreases from one time period to another, the object is undergoing a Deceleration (also called Negative Acceleration).
A car that moves at 10 miles per hour for the first minute, then at 20 miles per hour for the second minute, and finally at 30 miles per hour for the third minute, would be said to have a Uniform Acceleration of “10 miles per hour per minute”. If the car slowed down at the same rate it would be a Uniform Deceleration. If the rates of acceleration or deceleration vary from one time period to another, then it is said to have Variable Acceleration or VariableDeceleration.Doubts? A 6th-grade science tutor can help.
Acceleration = Final velocity – Starting velocity
Elapsed Time
For example, if a car accelerates from 0 miles per hour to 60 miles per hour in 30 seconds then the acceleration of the car would be –
Acceleration = | 60 – 0 30 | = 2 miles per hour per second |

Check Point
- ______ can change the motion or shape of an object.
- When an object changes its location in space, it is referred to as its ______.
- Motion is always in relation to some other place or object in the universe – it is with respect to a ________.
- ______ is the ratio of distance over time.
- When the velocity of an object increases from one time period to another, the object is said to undergo an _______.
Answer Key
- Force
- Motion
- Frame of Reference
- Speed
- Acceleration
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Pricing for Online Tutoring
| Tutoring Package | Validity | Grade (1-12), College |
|---|---|---|
| 5 sessions | 1 Month | $139 |
| 1 session | 1 Month | $28 |
| 10 sessions | 3 months | $269 |
| 15 sessions | 3 months | $399 |
| 20 sessions | 4 months | $499 |
| 50 sessions | 6 months | $1189 |
| 100 sessions | 12 months | $2249 |
6th Grade Free Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Adaptation
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Evolution
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Astronomy
- Ecology
- Energy
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Sound
- Light
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System
Images Credit:
https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2014/10/22/18/04/freerider-498473_1280.jpg
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/5b/Distancedisplacement.png
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird






