Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheets (Definition, Types and Examples)
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. It depends on the object’s mass and velocity, where higher mass and faster velocity result in greater kinetic energy. On the other hand, potential energy is the energy stored within an object based on its position or configuration in a system. The potential energy can be associated with gravitational forces, elastic properties, or even chemical bonds. When the object’s position or configuration changes, this potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy or other forms of energy, following the principle of conservation of energy.
Put your knowledge to the test with this challenging 6th Grade Science Worksheet! Read each question carefully and choose the response that you feel is correct.
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Energy can be broadly classified as potential or kinetic energy.
- Potential energy is the energy stored in a body by virtue of its position.
- Kinetic energy is the energy in a body due to its motion.
Potential energy
The energy possessed by an object due to its relative position is called potential energy. It is the stored energy that is ready to use. It can be classified into – Doubts? A 6th-grade science tutor can help.
Potential energy
The energy possessed by an object due to its relative position is called potential energy. It is the stored energy that is ready to use. It can be classified into –
1) Gravitational potential energy –
An object suspended at height has gravitational potential energy. For example, a ball or a skier at a height. A raised hammer possesses gravitational potential energy that holds the ability to displace a nail (work).
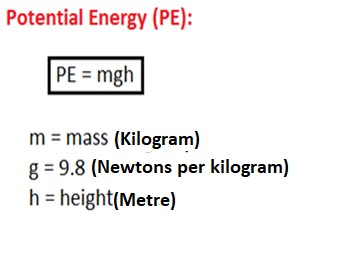
The higher and bigger in mass, the greater would be their potential energy! The potential energy can be calculated by multiplying the mass, acceleration due to gravity (a constant), and the height of the object.
Suppose you and your friends start skiing from the same height, who would have the maximum potential energy at the top? The lightest or the heaviest guy?


2) Magnetic Potential Energy –
We have learnt that opposite poles of two magnets attract and their like poles repel. The closer the opposite poles of two magnets, the more is the potential energy in them.
3) Chemical potential Energy –
The energy stored in food, fuels, batteries are examples of chemical energy. When we eat food, the chemical energy in food gets transformed to give us the energy to do mechanical work.
4) Elastic Energy –
Spring has more potential energy when it is compressed or stretched. For example, when we wind a mechanical clock, we are storing potential energy in its spring. As the spring loosens, energy is released slowly that turns the hands of the clock! When an arrow is placed in a bow with the string pulled back, the arrow has potential energy and can go far and even hurt someone (work).


5) Nuclear Energy –
The amount of energy released when atoms split is huge. This process is called nuclear fission and the energy released can be tapped to generate electricity.
eTutorWorld Understands Math Tutoring | Online Math Worksheets are Important Tools
Understanding graphs, charts, and opinion polls in a newspaper, for calculating house and car payments, and for choosing a long-distance telephone service are impossible without strong math skills …and the only way to develop strong math skills is by constant practice.
‘Practice makes a man perfect’ holds true for no other field better than for math. A middle or high school student must set aside a minimum of an hour for math every day. Other than textbooks, worksheets help you revise and understand concepts better.
Our expert tutors prepare online maths worksheets that are age and grade-appropriate. Grade-wise math worksheets for Elementary Math, Arithmetic, Pre-Algebra, Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Statistics, Pre-Calculus and Calculus can be solved to improve math skills, to get ahead or to even catch up.
You may download these FREE online math worksheets in the PDF format, and then print and email us their solutions for a free evaluation and analysis by eTutorworld’smath expert tutors.
You may solve these worksheets by yourself or with your peers while studying together.
The Answer Key at the end of each worksheet allows for a self-evaluation.
Personalized Online Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12, Test Prep help for Standardized tests like SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE and AP. You may schedule online tutoring lessons at your personal scheduled times, all with a Money-Back Guarantee. The first one-on-one online tutoring lesson is always FREE, no purchase obligation, no credit card required.
For answers/solutions to any question or to learn concepts, take a FREE CLASS.
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just book a free class to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Kinetic energy
Kinetic energy is the energy of mass in motion.
Kinetic energy can be classified into five types –
1) Radiant Energy –
Solar energy, light from bulbs and other lighting devices, heating elements in toasters and other appliances, x-rays, radio waves are examples of radiant kinetic energy that travel or move in waves or particles.

2) Thermal Energy –
While baking a pizza or boiling water, the molecules in them move as they release heat, they are examples of thermal energy.
3) Sound Energy –
Our voices, speakers, musical instruments, chirping of birds or any sound is caused by vibrations of particles. The source of sound creates waves that reach our eardrums through these vibrations.

4) Electrical Energy –
Electricity is the flow of electrons around a circuit. So there is movement all around us as we switch on the lights and heaters, it also means that all the electrical appliances in our houses work on this kinetic energy!
5) Mechanical Energy –
Any visible moving body around you possesses mechanical energy – a moving car, a moving ball, a running girl, a boy playing the piano with his moving fingers, etc. Aside from this, wind and a flowing river also have mechanical energy that we harness to generate electricity. Mechanical energy has two types of energy, such as potential and kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy depends on the mass and velocity of the object. The greater the mass and velocity, the greater would be the magnitude of kinetic energy.
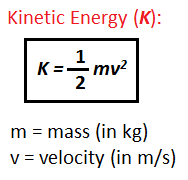
It can be represented as follows –

This means that if the velocity of the object doubles, it’s kinetic energy would quadruple!
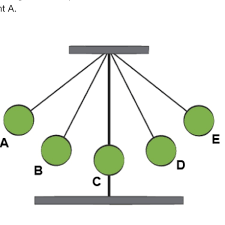
The potential and kinetic energy in a pendulum
Energy can be transformed from one form to another. The best example of potential energy converting into kinetic energy and vice versa is a pendulum. When we hold a pendulum on one side, it has a certain amount of potential energy. When we let it go, the pendulum will swing back and forth. The potential energy thus is converted into kinetic energy and back to potential and so on and so forth over and over again.
- At position A, the bob has potential energy. As the bob moves down to B and C, the potential energy starts to get converted into kinetic energy.
- At C, all the energy is converted into kinetic energy.
- At E all the energy is converted back to potential energy.
- At B and D, the bob has a combination of both.
Ideally, as per the law of conservation of energy, the bob should keep moving forever. But the bob eventually stops as it loses energy in the form of friction with air, heat, and sound.
Trivia: William Rankine of Scotland had introduced the term potential energy in 1853.
Check Point
- Indicate whether the following have potential or kinetic energy –
a) A stationary apple on a tree. b) Sunrays c) A speeding car
2. A sound is a form of kinetic energy that travels by _____ of particles around us.
3. Splitting of some atoms releases ____ energy.
4. A mechanical clock works with the help of _____ energy.
5. Potential energy depends upon the mass and ____ of the object.
Answer Key
- a) P.E. b) K.E. c) K.E.
- vibrations
- nuclear
- chemical
- height
What is kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. It is directly proportional to the mass and square of the velocity of the object. When an object is in motion, it has the potential to do work and cause changes in its surroundings.
What is potential energy?
Potential energy is the energy stored within an object based on its position or configuration relative to its surroundings. It can be associated with gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, or chemical potential energy, depending on the forces or interactions involved.
How are kinetic and potential energy related?
The relationship between kinetic and potential energy lies in the principle of conservation of energy. As an object moves, potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy and vice versa. For example, when a ball is thrown upwards, it gains potential energy due to its increased height, and as it falls back down, that potential energy converts into kinetic energy.
Can potential energy be negative?
Yes, potential energy can be negative depending on the reference point chosen. For instance, when an object is at a lower level compared to a chosen reference point, its gravitational potential energy is negative because it would require work to move the object upward to the reference point.
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Pricing for Online Tutoring
| Tutoring Package | Validity | Grade (1-12), College |
|---|---|---|
| 5 sessions | 1 Month | $139 |
| 1 session | 1 Month | $28 |
| 10 sessions | 3 months | $269 |
| 15 sessions | 3 months | $399 |
| 20 sessions | 4 months | $499 |
| 50 sessions | 6 months | $1189 |
| 100 sessions | 12 months | $2249 |
6th Grade Free Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Adaptation
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Evolution
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Astronomy
- Ecology
- Energy
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Sound
- Light
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System
Image Credits –
https://learnenglishkids.britishcouncil.org/word-games/daily-routines
https://www.atkinsongraphic.com
https://cpsbla.org/transportation/
https://www.theclockdepot.com/Cuckoo_Clocks.html
http://max.cs.kzoo.edu/gifs/tools/index.html
http://theproductiveteacher.org/mechanical-energy
https://scholars.unh.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1020&context=sustainability
https://okfirst.mesonet.org/train/meteorology/Radiation.html
https://www.physicscentral.org/experiment/physicsathome/drummingfingers.cfm
https://sciencetrek.org/sciencetrek/topics/force_and_motion/facts.cfm
https://brainly.com/question/10546232
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird






