Nuclear Energy
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
Nuclear energy is the energy that is released during nuclear reactions, which occur when the nuclei of atoms are split (nuclear fission) or combined (nuclear fusion).
Table of Contents:
- Nuclear Energy
- How does Nuclear Energy work?
- Nuclear Reactors & Fusions
- Types of Nuclear Reactions
- Safety of Nuclear Reactions
- Uses of Nuclear Energy
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy
- FAQs
Nuclear Energy - Grade 6 Science Worksheet PDF
This is a free printable / downloadable PDF worksheet with practice problems and answers. You can also work on it online.
|
Untimed | |
Sign up with your email ID to access this free worksheet.
"We really love eTutorWorld!"
"We really love etutorworld!. Anand S and Pooja are excellent math teachers and are quick to respond with requests to tutor on any math topic!" - Kieran Y (via TrustSpot.io)
"My daughter gets distracted easily"
"My daughter gets distracted very easily and Ms. Medini and other teachers were patient with her and redirected her back to the courses.
With the help of Etutorworld, my daughter has been now selected in the Gifted and Talented Program for the school district"
- Nivea Sharma (via TrustSpot.io)
Nuclear energy is the energy that is released during nuclear reactions, which occur when the nuclei of atoms are split (nuclear fission) or combined (nuclear fusion). These reactions produce enormous amounts of energy in the form of heat and light, which can be harnessed for a variety of applications, such as generating electricity and powering ships and submarines.
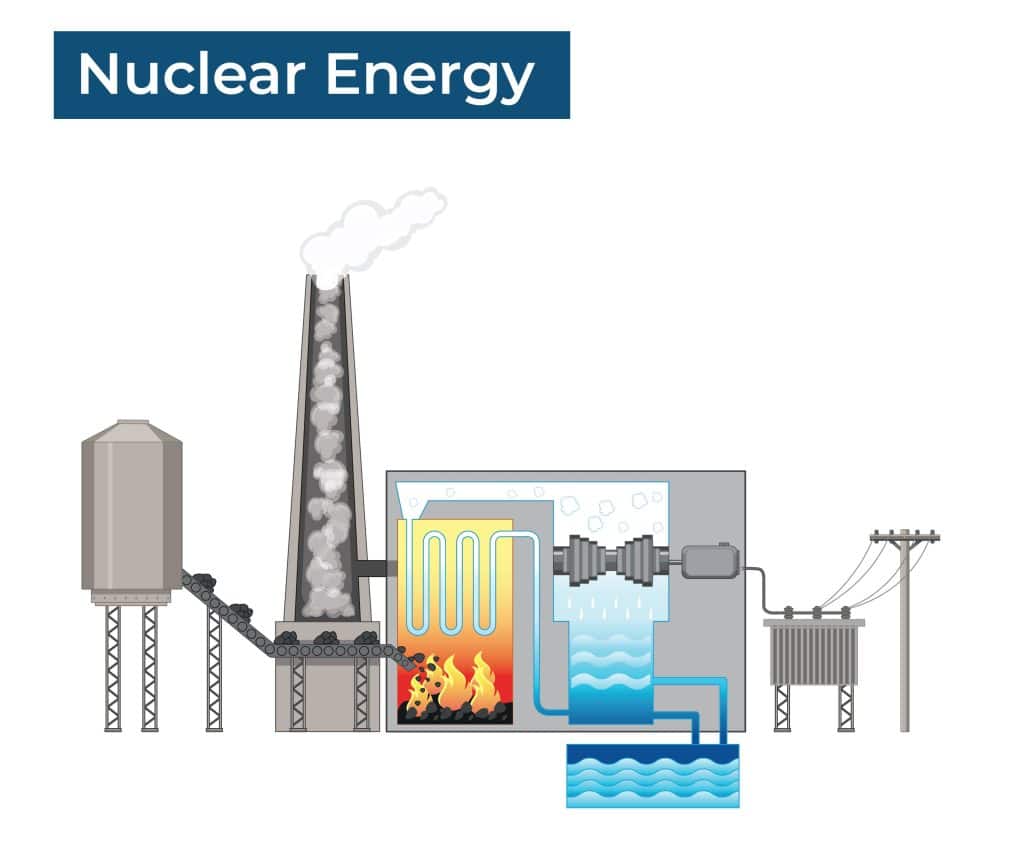
Nuclear energy is primarily produced in nuclear power plants, where controlled nuclear reactions are used to heat water and produce steam, which in turn drives turbines that generate electricity.
The fuel used in these reactions is typically uranium, which is a naturally occurring element that can be mined from the Earth’s crust.
Nuclear energy has several advantages over other forms of energy, including its high energy density, which means that it can produce large amounts of energy from a relatively small amount of fuel.
Nuclear energy is also a reliable and stable source of electricity, as it is not affected by changes in weather or other external factors.
However, nuclear energy also has several risks and challenges, including the potential for accidents and the storage and disposal of nuclear waste. These risks have led to significant public concerns and opposition to the use of nuclear energy in some countries.
Overall, nuclear energy is a complex and controversial topic, and its use and potential for the future continue to be the subject of much debate and discussion in scientific, political, and social circles
How does Nuclear Energy work?
Nuclear energy works by harnessing the energy released during nuclear reactions, which occur when the nucleus of an atom is split (nuclear fission) or combined (nuclear fusion). In both cases, the reaction releases a tremendous amount of energy in the form of heat and light.
In a nuclear power plant, nuclear energy is produced through controlled nuclear fission reactions. The process begins with uranium fuel rods, which are placed in the reactor core. When the uranium atoms in the fuel rods are bombarded with neutrons, they undergo fission or split into two smaller nuclei, releasing a large amount of energy in the process.
This energy is in the form of heat, which is used to generate steam. The steam then drives a turbine that is connected to a generator, which produces electricity. The heat is then removed from the system using a coolant, such as water, which circulates through the reactor core and transfers the heat to a heat exchanger.
In a nuclear fusion reaction, lighter elements, such as hydrogen, are combined to form heavier elements, such as helium. This process releases a tremendous amount of energy, much more than in a fission reaction. However, nuclear fusion is much more difficult to achieve and has not yet been harnessed for commercial use.
While nuclear energy has the potential to produce large amounts of electricity, it also carries several risks and challenges, including the potential for accidents, the storage and disposal of nuclear waste, and the potential for nuclear weapons proliferation. These risks must be carefully managed and addressed to ensure the safe and effective use of nuclear energy.
Nuclear Reactors & Fusions
Nuclear fusion is a process in which two atomic nuclei come together to form a heavier nucleus, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. This process is the source of energy in stars and has the potential to provide a virtually limitless supply of clean and sustainable energy on Earth.
Nuclear fusion reactors are devices designed to harness the energy produced by nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion reactor, hydrogen isotopes, such as deuterium and tritium, are heated to extreme temperatures and pressures, causing them to collide and fuse into helium atoms. This process releases a large amount of energy in the form of heat, which can be used to generate electricity.
One of the main advantages of nuclear fusion over nuclear fission is that fusion reactions do not produce the long-lived radioactive waste that is produced by fission reactions. Additionally, the fuel for fusion reactions, such as deuterium, is abundant and can be extracted from seawater.
However, nuclear fusion is a complex and challenging process that requires extremely high temperatures and pressures to be maintained for extended periods of time. Researchers and engineers around the world are working to develop practical and reliable fusion reactors, but significant scientific and technical challenges remain.
Nuclear fission reactors, on the other hand, are devices that harness the energy released by nuclear fission reactions. These reactors use uranium or other fissile materials to sustain a chain reaction of fission reactions, which release a large amount of energy in the form of heat. This heat is used to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity.
Nuclear fission reactors are currently used to generate a significant portion of the world’s electricity, but they also carry several risks and challenges, including the potential for accidents and the storage and disposal of radioactive waste. The safe and effective use of nuclear fission reactors requires careful management and oversight.
Types of Nuclear Reactions
Nuclear fission is a process in which the nucleus of an atom is split into two or more smaller nuclei, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. This is the process used in nuclear power plants to generate electricity.
Nuclear fusion is a process in which two atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. This is the process that powers the sun and other stars, and has the potential to provide a virtually limitless supply of clean and sustainable energy on Earth.
Both types of nuclear reactions have the potential to produce large amounts of energy, but they also carry risks and challenges. Nuclear fission reactions can produce radioactive waste and the potential for accidents, while nuclear fusion reactions require extremely high temperatures and pressures to be sustained for extended periods of time, which is a significant scientific and technical challenge.
Safety of Nuclear Reactions
In terms of safety, nuclear energy can be dangerous if not managed properly. The potential for accidents, such as those that occurred at Chernobyl and Fukushima, highlights the need for careful management and oversight of nuclear facilities. Additionally, the storage and disposal of nuclear waste is a significant challenge, as the waste can remain radioactive for thousands of years.
However, when managed properly, nuclear energy can be a safe and effective source of electricity. The development of advanced reactor designs and improved safety measures can help to mitigate the risks associated with nuclear energy, while also helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and provide a reliable source of electricity.
“There have been times when we booked them last minute, but the teachers have been extremely well-prepared and the help desk at etutorworld is very prompt.
Our kid is doing much better with a higher score.”
6th Grade Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers Personalized Online Tutoring for Math, Science, English, and Standardised Tests.
Our Tutoring Packs start at just under $22.49 per hour, and come with a moneyback guarantee.
Schedule a FREE Trial Session, and experience quality tutoring for yourself. (No credit card required.)
Uses of Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy has a variety of uses, including:
1. Electricity generation: Nuclear power plants are used to generate electricity by harnessing the energy produced by nuclear fission reactions. These power plants can produce large amounts of electricity with very low greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Medical applications: Nuclear energy is used in medicine for a variety of applications, including radiation therapy for cancer treatment, medical imaging, and sterilization of medical equipment.
3. Space exploration: Nuclear power is used to power spacecraft and space probes, which need a reliable and long-lasting source of energy to operate in deep space.
4. Industrial applications: Nuclear energy can be used in a variety of industrial applications, including food irradiation and the sterilization of medical and industrial equipment.
5. Military applications: Nuclear energy is used in the production of nuclear weapons and in the propulsion systems of some military submarines and aircraft carriers.
While nuclear energy has many potential uses, it is important to manage its risks and ensure that it is used safely and responsibly. This includes careful management of nuclear waste and ensuring the safety of nuclear facilities to prevent accidents and other incidents.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy
Advantages of Nuclear Energy:
- Nuclear energy is a reliable and stable source of electricity, as it is not affected by changes in weather or other external factors.
- It has a high energy density, which means that it can produce large amounts of energy from a relatively small amount of fuel.
- Nuclear power plants emit fewer greenhouse gases than fossil fuel power plants, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Nuclear power plants can be located near population centers, reducing the need for long-distance transmission lines.
- Nuclear energy can be used to power space exploration, such as for manned missions to Mars.
Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy:
- The potential for accidents, such as the Chernobyl and Fukushima disasters, which can have serious health and environmental consequences.
- The storage and disposal of nuclear waste, which remains radioactive for thousands of years and poses a significant risk to human health and the environment.
- The risk of nuclear weapons proliferation, as nuclear technology can be used to produce weapons-grade materials.
- The high cost of building and maintaining nuclear power plants.
- Public concerns and opposition to the use of nuclear energy, which can make it difficult to gain public support and investment
Do You Stack Up Against the Best?
If you have 30 minutes, try our free diagnostics test and assess your skills.
Nuclear Energy FAQS
What is nuclear energy?
Nuclear energy is the energy released by a nuclear reaction, either through nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. It can be harnessed to generate electricity and has many other uses in medicine, industry, and space exploration.
How is nuclear energy generated?
Nuclear energy is generated through nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. In nuclear fission, the nucleus of an atom is split, releasing a large amount of energy. In nuclear fusion, two atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing a large amount of energy.
What is a nuclear reactor?
A nuclear reactor is a device that uses nuclear reactions to generate heat, which can be used to produce electricity. The reactor contains fuel rods that undergo nuclear fission, releasing heat that is used to boil water and create steam, which then drives a turbine to generate electricity.
Is nuclear energy safe?
Nuclear energy can be safe if it is managed properly. The potential for accidents, such as those at Chernobyl and Fukushima, highlight the need for careful management and oversight of nuclear facilities. Additionally, the storage and disposal of nuclear waste is a significant challenge.
What is nuclear waste?
Nuclear waste is the radioactive material that is left over after nuclear reactions, including nuclear fission in nuclear reactors. The waste can remain radioactive for thousands of years and poses a significant challenge for storage and disposal.
How is nuclear energy regulated?
Nuclear energy is highly regulated by government agencies, including the Nuclear Regulatory Commission in the United States. These agencies oversee the construction and operation of nuclear facilities, ensure the safety of workers and the public, and manage the storage and disposal of nuclear waste.
Can nuclear energy help combat climate change?
Nuclear energy can be a low-carbon energy source that can help combat climate change. Nuclear power plants emit very little greenhouse gases during operation and can provide a reliable source of electricity without relying on fossil fuels. However, the risks and challenges associated with nuclear energy must be carefully managed.

Kathleen Currence is one of the founders of eTutorWorld. Previously a middle school principal in Kansas City School District, she has an MA in Education from the University of Dayton, Ohio. She is a prolific writer, and likes to explain Science topics in student-friendly language. LinkedIn Profile
Affordable Tutoring Now Starts at Just $22.49
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12. We are also a leading provider of Test Prep help for Standardized Tests (SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE, and AP).
What makes eTutorWorld stand apart are: flexibility in lesson scheduling, quality of hand-picked tutors, assignment of tutors based on academic counseling and diagnostic tests of each student, and our 100% money-back guarantee.
Whether you have never tried personalized online tutoring before or are looking for better tutors and flexibility at an affordable price point, schedule a FREE TRIAL Session with us today.
*There is no purchase obligation or credit card requirement
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Adaptation
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Evolution
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Astronomy
- Ecology
- Energy
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Sound
- Light
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird










