Chemical Properties of Matter
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
Chemical properties of matter refer to the ability of a substance to change its chemical composition or chemical identity when it reacts with other substances. These properties can be observed through chemical reactions, and they can be used to predict how a substance will behave in different situations.
Grade 6 Science Worksheet PDF
This is a free printable / downloadable PDF worksheet with practice problems and answers. You can also work on it online.
|
Untimed | |
Sign up with your email ID to access this free worksheet.
"We really love eTutorWorld!"
"We really love etutorworld!. Anand S and Pooja are excellent math teachers and are quick to respond with requests to tutor on any math topic!" - Kieran Y (via TrustSpot.io)
"My daughter gets distracted easily"
"My daughter gets distracted very easily and Ms. Medini and other teachers were patient with her and redirected her back to the courses.
With the help of Etutorworld, my daughter has been now selected in the Gifted and Talented Program for the school district"
- Nivea Sharma (via TrustSpot.io)
Examples of chemical properties include:
- Reactivity: The ability of a substance to participate in chemical reactions.
- Combustibility: The ability of a substance to burn or support combustion.
- Oxidation: The ability of a substance to gain or lose electrons.
- Acidity: The ability of a substance to donate or accept protons.
- Toxicity: The ability of a substance to cause harm or death to live organisms.
Chemical properties are different from physical properties which are characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance. Understanding chemical properties is important for fields such as chemistry, materials science, and engineering, as well as in everyday life, for example, food preservation, environmental protection, and medicine.
1. Reactivity
Reactivity is a chemical property of matter that refers to the ability of a substance to participate in chemical reactions. It describes how readily a substance will react with other substances to form new compounds.
Some examples of reactivity include:
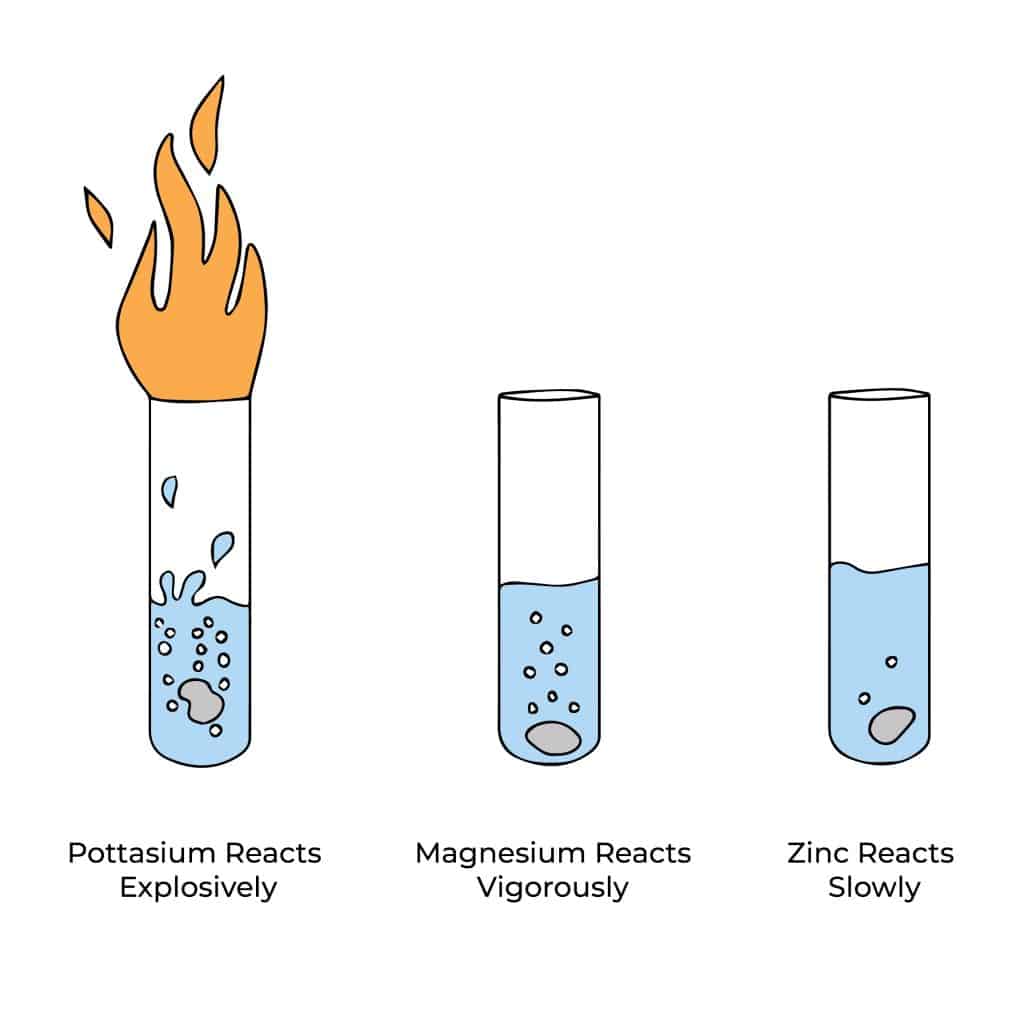
- The reactivity of metals, such as sodium and potassium, readily reacts with water to form metal hydroxides and hydrogen gas.
- The reactivity of acids, such as hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, readily reacts with bases to form salt and water.
- The reactivity of gases, such as oxygen and methane, readily reacts with each other to form water and carbon dioxide.
Reactivity can also be influenced by various factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of catalysts or inhibitors. Some substances are highly reactive, while others are relatively unreactive. Understanding the reactivity of a substance is important in many fields, such as chemistry, materials science, and engineering, as well as every day.
2. Combustibility
Combustibility is a chemical property of matter that refers to the ability of a substance to burn or support combustion. It describes how readily a substance will react with oxygen to form new compounds, typically in the form of heat, light and other gases.
Some examples of combustibility include:
- The combustibility of fuels such as gasoline, propane, and natural gas, which burn readily when exposed to air or oxygen.
- The combustibility of wood, paper, and other organic materials, which burn readily when exposed to air or oxygen.
- The combustibility of certain chemicals, such as sodium, which can ignite and burn when exposed to air or water.
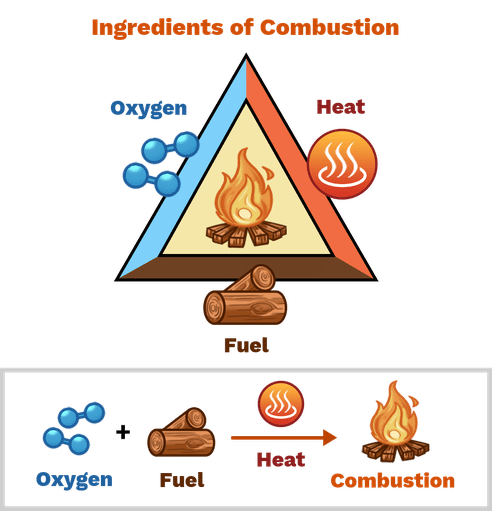
Combustibility can also be influenced by various factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of other chemicals, like catalysts or inhibitors. Some substances are highly combustible, while others are relatively non-combustible. Understanding the combustibility of a substance is important in many fields such as materials science, fire safety, and engineering, as well as in everyday life, for example, when using flammable liquids or when deciding which materials to use for building construction.
3. Oxidation
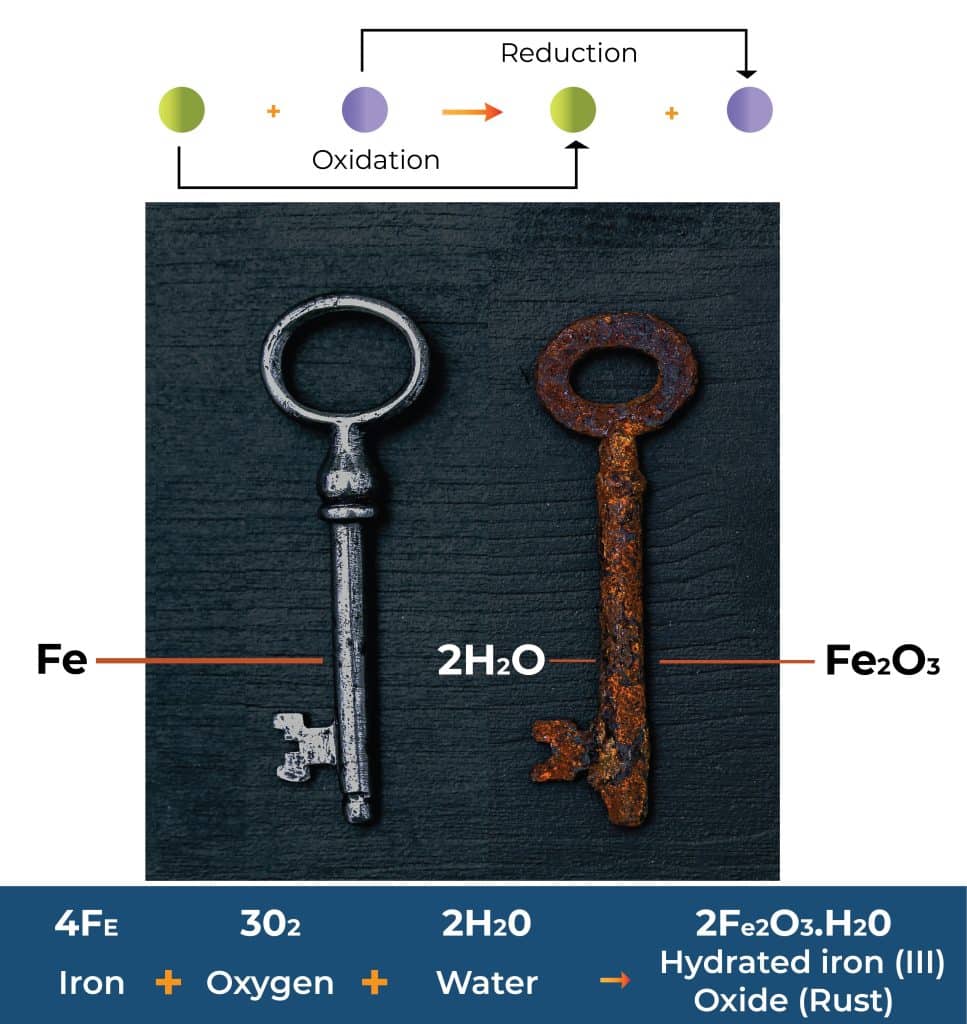
Oxidation is a chemical property of matter that refers to the ability of a substance to gain or lose electrons during a chemical reaction. When a substance loses electrons, it is said to be oxidized, and when a substance gains electrons, it is said to be reduced. This process is called oxidation-reduction or redox reaction.
Some examples of oxidation include:
- The oxidation of metals, such as iron, which can rust when exposed to air and water. This is because iron loses electrons to oxygen, forming iron oxide (rust).
- The oxidation of organic materials, such as wood, which can burn when exposed to air and heat. This is because wood loses electrons to oxygen, forming carbon dioxide and water.
On the other hand, an example of reduction is:
- The reduction of metal oxides, such as iron oxide, which can be reduced to iron by exposure to a reducing agent such as carbon monoxide.
Understanding oxidation and reduction reactions are important in many fields such as chemistry, materials science, and engineering, as well as in everyday life, for example, in the treatment of wastewater and air pollution, and in the production of metals and other materials.
4. Acidity
Acidity is a chemical property of matter that refers to the ability of a substance to donate or accept protons (hydrogen ions, H+) during a chemical reaction. Substances that can donate protons are known as acids, and substances that can accept protons are known as bases. This process is known as an acid-base reaction.
Acids are characterized by their pH values, which range from 0 to 14. Substances with a pH less than 7 are considered acidic, and those with a pH greater than 7 are considered basic (or alkaline).
Some examples of acids include:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a strong acid and has a pH of less than 1
- Citric acid which is found in lemons and limes, has a pH of 2-3
Some examples of bases include:
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a strong base and has a pH of 14
- Ammonia (NH3) has a pH of 11-12.
Understanding acid-base reactions is important in many fields such as chemistry, biology, materials science, and engineering, as well as in everyday life, for example, in the food and beverage industry, in the treatment of wastewater and air pollution, and in the production of fertilizers and cleaning agents.
“There have been times when we booked them last minute, but the teachers have been extremely well-prepared and the help desk at etutorworld is very prompt.
Our kid is doing much better with a higher score.”
6th Grade Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers Personalized Online Tutoring for Math, Science, English, and Standardised Tests.
Our Tutoring Packs start at just under $22.49 per hour, and come with a moneyback guarantee.
Schedule a FREE Trial Session, and experience quality tutoring for yourself. (No credit card required.)
5. Toxicity
Toxicity is a chemical property of matter that refers to the ability of a substance to cause harm or death to living organisms. Toxicity can occur through various routes of exposure such as ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact. The degree of toxicity can vary depending on the substance and the route of exposure.
Some examples of toxic substances include:
- Heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and cadmium can cause damage to the nervous system, kidneys, and other organs if ingested or inhaled in high amounts.
- Pesticides and herbicides, such as glyphosate and organophosphates, can cause damage to the nervous system and other organs if ingested or inhaled in high amounts.
- Carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless gas produced by combustion, can cause headaches, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and even death if inhaled in high concentrations.
Toxicity can also vary depending on the dose, duration of exposure and the susceptibility of the organism. Understanding toxicity and the risks associated with exposure to toxic substances is important in many fields such as chemistry, biology, public health, and environmental science, as well as in everyday life, for example, when handling chemicals, cleaning products, and food.
Do You Stack Up Against the Best?
If you have 30 minutes, try our free diagnostics test and assess your skills.
Chemical Properties of Matter FAQS
What are the chemical properties of matter?
Chemical properties of matter refer to the ability of a substance to change its chemical composition or chemical identity when it reacts with other substances. These properties can be observed through chemical reactions, and they can be used to predict how a substance will behave in different situations.
How are chemical properties different from physical properties?
Chemical properties describe how a substance will react with other substances to form new compounds, while physical properties are characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance.
What are some examples of chemical properties?
Examples of chemical properties include reactivity, combustibility, oxidation, acidity, and toxicity.
What is the difference between an acid and a base?
Acids are substances that can donate protons and have a pH less than 7, bases are substances that can accept protons and have a pH greater than 7.
How can we measure chemical properties?
Chemical properties can be measured through various methods such as chemical reactions, pH measurements, and spectroscopy.
How does toxicity vary?
Toxicity can vary depending on the substance and the route of exposure, as well as the dose, duration of exposure, and the susceptibility of the organism.

Kathleen Currence is one of the founders of eTutorWorld. Previously a middle school principal in Kansas City School District, she has an MA in Education from the University of Dayton, Ohio. She is a prolific writer, and likes to explain Science topics in student-friendly language. LinkedIn Profile
Affordable Tutoring Now Starts at Just $22.49
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12. We are also a leading provider of Test Prep help for Standardized Tests (SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE, and AP).
What makes eTutorWorld stand apart are: flexibility in lesson scheduling, quality of hand-picked tutors, assignment of tutors based on academic counseling and diagnostic tests of each student, and our 100% money-back guarantee.
Whether you have never tried personalized online tutoring before or are looking for better tutors and flexibility at an affordable price point, schedule a FREE TRIAL Session with us today.
*There is no purchase obligation or credit card requirement
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Adaptation
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Evolution
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Astronomy
- Ecology
- Energy
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Sound
- Light
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird










