Area of a Trapezoid
Grade 6 Math Worksheets
A trapezoid is a four-sided geometric shape that has two parallel sides and two non-parallel sides. The parallel sides are called the bases, while the non-parallel sides are called the legs. The area of a trapezoid is the amount of space contained within its boundaries. It is important to know how to find the area of a trapezoid in order to use it in real-world applications, such as construction and engineering.
In this article, you will learn:
- The formula for finding the area of a trapezoid
- Steps for finding the area of a trapezoid
- Examples of finding the area of a trapezoid
- Tips for measuring the height and parallel side lengths
- FAQs
Area of a Trapezoid - Grade 6 Math Worksheet PDF
This is a free printable / downloadable PDF worksheet with practice problems and answers. You can also work on it online.
|
Untimed | |
Sign up with your email ID to access this free worksheet.
"We really love eTutorWorld!"
"We really love etutorworld!. Anand S and Pooja are excellent math teachers and are quick to respond with requests to tutor on any math topic!" - Kieran Y (via TrustSpot.io)
"My daughter gets distracted easily"
"My daughter gets distracted very easily and Ms. Medini and other teachers were patient with her and redirected her back to the courses.
With the help of Etutorworld, my daughter has been now selected in the Gifted and Talented Program for the school district"
- Nivea Sharma (via TrustSpot.io)
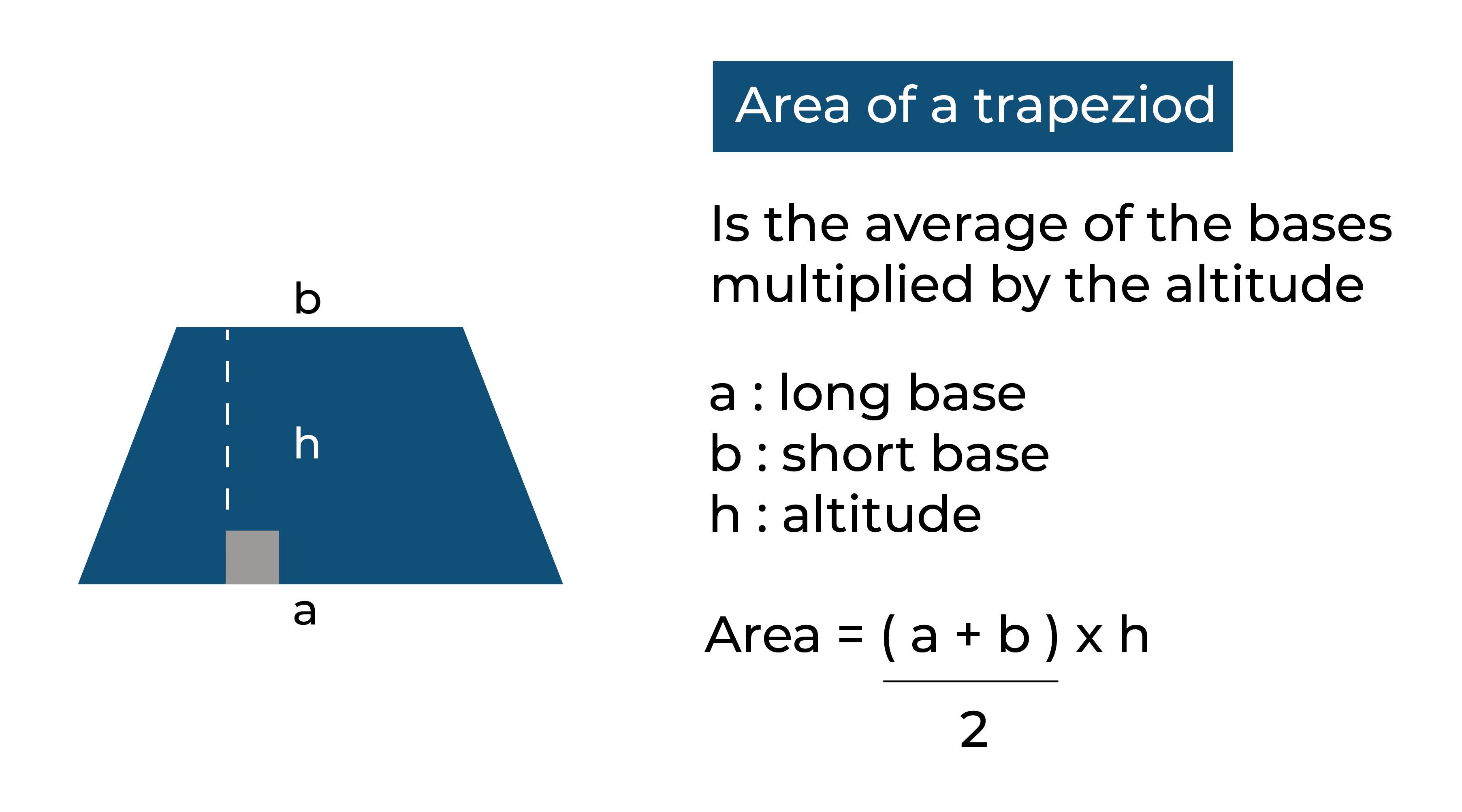
The formula for finding the area of a trapezoid
A = (b1 + b2)/2 * h,
where A is the area of the trapezoid, b1 and b2 are the lengths of the two parallel sides, and h is the height of the trapezoid.
Steps for finding the area of a trapezoid
The first step in finding the area of a trapezoid is to measure the height of the trapezoid. The height is the perpendicular distance between the two parallel sides.
Next, measure the lengths of the two parallel sides of the trapezoid. This will give you the values for b1 and b2 in the formula.
Next, find the average of the two parallel side lengths by adding them together and dividing by two. This is the value that you will use for b in the formula.
Finally, multiply the height and average length to find the area of the trapezoid. This result will give you the total area of the trapezoid in square units.
“There have been times when we booked them last minute, but the teachers have been extremely well-prepared and the help desk at etutorworld is very prompt.
Our kid is doing much better with a higher score.”
6th Grade Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers Personalized Online Tutoring for Math, Science, English, and Standardised Tests.
Our Tutoring Packs start at just under $22.49 per hour, and come with a moneyback guarantee.
Schedule a FREE Trial Session, and experience quality tutoring for yourself. (No credit card required.)
Examples of finding the area of a trapezoid
Example 1: Finding the area of a trapezoid with known height and parallel side lengths
Suppose you have a trapezoid with a height of 8 units and parallel side lengths of 10 units and 16 units. To find the area of the trapezoid, use the formula:
A = (b1 + b2)/2 * h = (10 + 16)/2 * 8 = 13 * 8 = 104 square units.
Example 2: Finding the area of a trapezoid with known height and diagonals
Suppose you have a trapezoid with a height of 10 units and diagonals that measure 15 units and 20 units. To find the area of the trapezoid, use the following steps:
First, find the lengths of the parallel sides by using the Pythagorean theorem.
a^2 + b^2 = c^2
(b1/2)^2 + h^2 = (d1/2)^2
(b2/2)^2 + h^2 = (d2/2)^2
Solving for b1 and b2, you get:
b1 = √(d1^2 – h^2) = √(225 – 100) = √125 = 11.18 units
b2 = √(d2^2 – h^2) = √(400 – 100) = √300 = 17.32 units
Use the formula to find the area:
A = (b1 + b2)/2 * h = (11.18 + 17.32)/2 * 10 = 14.25 * 10 = 142.5 square units
Accurate measurement of the height and parallel side lengths is crucial when finding the area of a trapezoid. Any measurement errors can result in a significant difference in the calculated area. It is important to use precise tools and techniques to ensure accurate measurements.
Tips for measuring the height and parallel side lengths
When measuring the height of a trapezoid, it is important to use a ruler or measuring tape to ensure that the measurement is as precise as possible. Measure the height at several points along the trapezoid to ensure that the measurement is consistent.
For measuring the parallel side lengths of the trapezoid, it is best to use a ruler or measuring tape. If the trapezoid is large, use a laser distance meter to get the most accurate measurements.
Importance of using a ruler or measuring tape to measure the height and parallel side lengths
Using a ruler or measuring tape to measure a trapezoid’s height and parallel side lengths is important because these tools provide the most accurate measurements. Measuring by eye or with other tools can result in significant errors that can affect the calculated area of the trapezoid.
The steps involved in finding the area of a trapezoid include measuring the trapezoid’s height and parallel side lengths, finding the average of the parallel side lengths, and using the formula A = (b1 + b2)/2 * h to calculate the area.
Finding the area of a trapezoid is an important mathematical skill that can be used in a variety of real-world applications. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can find the area of a trapezoid accurately and efficiently. It is important to use precise tools and techniques to ensure that the measurements are accurate, and to follow the formula A = (b1 + b2)/2 * h to calculate the area.
Do You Stack Up Against the Best?
If you have 30 minutes, try our free diagnostics test and assess your skills.
Area of a Trapezoid FAQS
What is a trapezoid?
A trapezoid is a 2-dimensional geometric shape with one pair of parallel and two non-parallel sides.
How do you find the area of a trapezoid?
To find the area of a trapezoid, you need to measure the height and parallel side lengths of the trapezoid, find the average of the parallel side lengths, and then use the formula A = (b1 + b2)/2 * h to calculate the area.
What is the formula for finding the area of a trapezoid?
The formula for finding the area of a trapezoid is A = (b1 + b2)/2 * h, where b1 and b2 are the parallel side lengths and h is the height of the trapezoid.
Why is it important to accurately measure a trapezoid's height and parallel side lengths when finding the area?
Accurate measurement of the height and parallel side lengths is important because any measurement errors can result in a significant difference in the calculated area.
What is the best tool for measuring a trapezoid's height and parallel side lengths?
The best tool for measuring a trapezoid’s height and parallel side lengths is a ruler or measuring tape. If the trapezoid is large, a laser distance meter may be helpful for getting the most accurate measurements.

Gloria Mathew writes on math topics for K-12. A trained writer and communicator, she makes math accessible and understandable to students at all levels. Her ability to explain complex math concepts with easy to understand examples helps students master math. LinkedIn
Affordable Tutoring Now Starts at Just $22.49
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12. We are also a leading provider of Test Prep help for Standardized Tests (SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE, and AP).
What makes eTutorWorld stand apart are: flexibility in lesson scheduling, quality of hand-picked tutors, assignment of tutors based on academic counseling and diagnostic tests of each student, and our 100% money-back guarantee.
Whether you have never tried personalized online tutoring before or are looking for better tutors and flexibility at an affordable price point, schedule a FREE TRIAL Session with us today.
*There is no purchase obligation or credit card requirement
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Adaptation
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Evolution
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Astronomy
- Ecology
- Energy
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Sound
- Light
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird










