Greenhouse Effect
Grade 7 Science Worksheets
The greenhouse effect refers to the process by which certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap heat from the sun, leading to a warming of the planet’s surface.
Table of Contents:
- Greenhouse Effect
- Example
- Causes of Greenhouse Effect
- Effects of Greenhouse Effect
- How to reduce Greenhouse Effect
- FAQs
Greenhouse Effect - Grade 7 Science Worksheet PDF
This is a free printable / downloadable PDF worksheet with practice problems and answers. You can also work on it online.
|
Untimed | |
Sign up with your email ID to access this free worksheet.
"We really love eTutorWorld!"
"We really love etutorworld!. Anand S and Pooja are excellent math teachers and are quick to respond with requests to tutor on any math topic!" - Kieran Y (via TrustSpot.io)
"My daughter gets distracted easily"
"My daughter gets distracted very easily and Ms. Medini and other teachers were patient with her and redirected her back to the courses.
With the help of Etutorworld, my daughter has been now selected in the Gifted and Talented Program for the school district"
- Nivea Sharma (via TrustSpot.io)
The greenhouse effect refers to the process by which certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap heat from the sun, leading to a warming of the planet’s surface.
The greenhouse gases (e.g. carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor) absorb and re-emit some of the infrared radiation that is radiated from the Earth’s surface back into the atmosphere.
While water vapor is a greenhouse gas, it is not directly influenced by human activities like carbon dioxide and methane. It is important to note that the increase in other greenhouse gases indirectly affects water vapor levels, as warmer temperatures caused by these gases can lead to more water vapor in the atmosphere, amplifying the greenhouse effect. As a result, more heat is retained in the atmosphere, leading to an increase in temperature.

This process is similar to how a greenhouse functions, hence the name “greenhouse effect.” In a greenhouse, glass walls trap heat inside, allowing plants to thrive in a warmer environment. Similarly, greenhouse gases trap heat inside the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to a warming of the planet’s surface.
Examples of Greenhouse Effects
Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth’s average temperature would be around -18°C (0°F). However, due to the presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature is around 15°C (59°F).
Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and agriculture have increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to an increase in the strength of the greenhouse effect and a warming of the planet’s surface.
Venus, the second planet from the sun, has a surface temperature of around 460°C (860°F) due to an extreme greenhouse effect caused by its thick atmosphere rich in carbon dioxide.
Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere through the greenhouse effect. These gases absorb and re-emit some of the infrared radiation that is radiated from the Earth’s surface back into the atmosphere, leading to an increase in temperature. The most common greenhouse gases include:
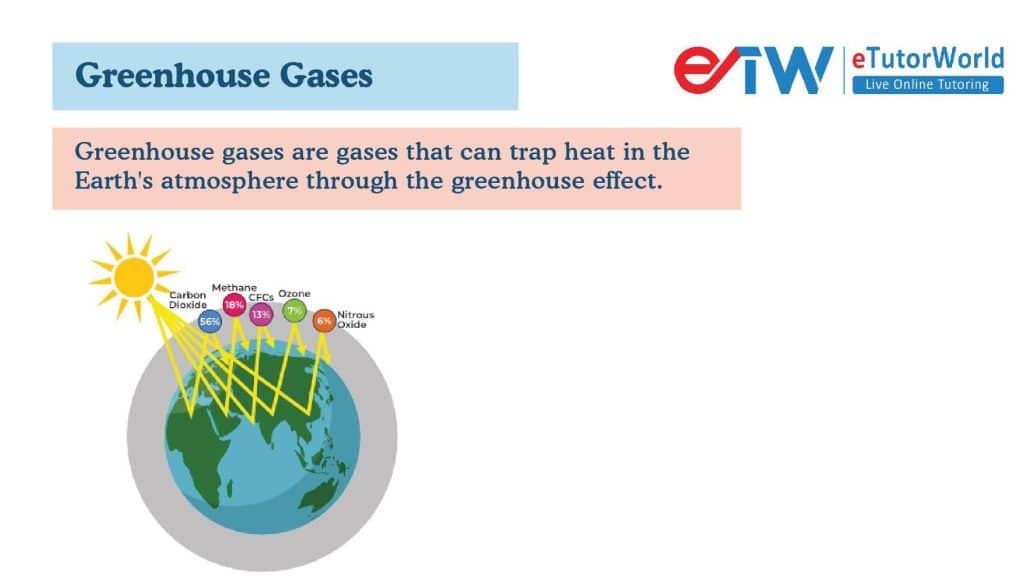
Carbon dioxide (CO2): This is the most significant greenhouse gas in terms of its contribution to the greenhouse effect. It is released into the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas, as well as deforestation and land-use changes.
Methane (CH4): This gas is emitted through natural processes such as the decay of organic matter and human activities such as livestock farming and the production and transport of fossil fuels.
Nitrous oxide (N2O): This gas is released through agricultural practices such as the use of synthetic fertilizers, as well as through the burning of fossil fuels.
Fluorinated gases: This is a group of gases that includes hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6). These gases are released through a variety of human activities such as refrigeration, air conditioning, and semiconductor production.
Overall, greenhouse gases play an important role in regulating the Earth’s temperature and making the planet habitable for life as we know it. However, the increase in greenhouse gas concentrations due to human activities has led to an enhancement of the greenhouse effect, causing global warming and climate change.
Causes of Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is caused by the presence of certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere that trap heat from the sun, leading to a warming of the planet’s surface. The main causes of the enhanced greenhouse effect, which is the current situation where greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are increasing, include:
Burning of Fossil Fuels: The primary cause of the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas for transportation, heating, and electricity generation. This releases large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Deforestation: Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their biomass. Deforestation, therefore, reduces the ability of the land to absorb carbon dioxide and contributes to the buildup of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, so protecting and restoring forests can help mitigate the greenhouse effect.
Agricultural Activities: Livestock farming and the use of synthetic fertilizers in agriculture can produce significant amounts of methane and nitrous oxide, respectively, which are potent greenhouse gases.
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes release greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and fluorinated gases into the atmosphere.
Land-Use Changes: Changes in land use, such as the conversion of forested land to agricultural land or urban areas, can release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Overall, human activities are the primary cause of the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to a strengthening of the greenhouse effect and contributing to global warming and climate change.
Effects of Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect, when it occurs naturally, plays an important role in regulating the Earth’s temperature and making the planet habitable for life as we know it. However, the enhanced greenhouse effect, which is the current situation where greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere are increasing due to human activities, can have a number of negative effects on the environment and society, including:
Global warming: The increase in temperature caused by the enhanced greenhouse effect can lead to global warming, which has a range of impacts such as melting of glaciers, sea-level rise, and more frequent and severe heatwaves, droughts, and extreme weather events.
Changes in precipitation patterns: Climate change caused by the enhanced greenhouse effect can also cause changes in precipitation patterns, leading to more frequent and severe floods, storms, and droughts, which can have serious impacts on agriculture, water availability, and infrastructure.
Biodiversity loss: The changing climate can also affect ecosystems and lead to the loss of biodiversity, as some species are unable to adapt to the changing conditions.
Human health impacts: The changing climate can also have significant impacts on human health, such as an increased risk of heat-related illness, the spread of vector-borne diseases, and the deterioration of air and water quality.
Economic impacts: Climate change caused by the enhanced greenhouse effect can have significant economic impacts, such as loss of productivity in agriculture, increased costs of infrastructure damage and repair, and reduced tourism.
Overall, the negative impacts of the enhanced greenhouse effect highlight the importance of taking action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.
“There have been times when we booked them last minute, but the teachers have been extremely well-prepared and the help desk at etutorworld is very prompt.
Our kid is doing much better with a higher score.”
7th Grade Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers Personalized Online Tutoring for Math, Science, English, and Standardised Tests.
Our Tutoring Packs start at just under $21 per hour, and come with a moneyback guarantee.
Schedule a FREE Trial Session, and experience quality tutoring for yourself. (No credit card required.)
How to reduce Greenhouse Effect?
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is a key strategy for mitigating the negative effects of the enhanced greenhouse effect. Here are some examples of strategies that can be used to reduce greenhouse gas emissions:
Use of renewable energy: Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and geothermal power can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the electricity sector.
Energy efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industry can reduce energy demand and therefore reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Public transportation and alternative transportation: Encouraging the use of public transportation, cycling, walking, and electric vehicles can reduce emissions from transportation.
Plant trees and protect forests: Planting trees and protecting forests can help to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and reduce greenhouse gas emissions from deforestation.
Reduce food waste: Reducing food waste can reduce methane emissions from landfills.
Use of low-carbon technologies: Implementing low-carbon technologies such as carbon capture and storage, and advanced nuclear power can also help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.Investing in research and development for clean energy technologies, carbon capture and storage, and other innovative solutions can accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy and help mitigate the greenhouse effect.
Carbon pricing: Implementing policies such as a carbon tax or a cap-and-trade system can help to incentivize the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by placing a price on carbon. There are international agreements like the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global temperature rise by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, can emphasize the global efforts to address the greenhouse effect and the importance of international cooperation.
Overall, reducing greenhouse gas emissions will require a combination of policies, technologies, and behavioral changes to be effective.
Do You Stack Up Against the Best?
If you have 30 minutes, try our free diagnostics test and assess your skills.
Greenhouse Effect FAQS
What is the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is a natural process in which certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap heat from the sun and keep the planet warm enough to support life.
What is the enhanced greenhouse effect?
The enhanced greenhouse effect is the current situation where human activities are causing an increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to a strengthening of the greenhouse effect and contributing to global warming and climate change.
What are greenhouse gases?
Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth’s atmosphere that trap heat from the sun and contribute to the greenhouse effect. The main greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide.
What are the negative effects of the enhanced greenhouse effect?
The negative effects of the enhanced greenhouse effect include global warming, changes in precipitation patterns, loss of biodiversity, human health impacts, and economic impacts.
What can be done to reduce greenhouse gas emissions?
Strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions include using renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, promoting alternative transportation, planting trees and protecting forests, reducing food waste, using low-carbon technologies, and implementing carbon pricing policies.
Why is it important to reduce greenhouse gas emissions?
It is important to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the negative effects of the enhanced greenhouse effect and prevent further climate change. This includes reducing the risk of catastrophic impacts such as sea-level rise, more frequent and severe natural disasters, and food and water shortages.

Kathleen Currence is one of the founders of eTutorWorld. Previously a middle school principal in Kansas City School District, she has an MA in Education from the University of Dayton, Ohio. She is a prolific writer, and likes to explain Science topics in student-friendly language. LinkedIn Profile
Affordable Tutoring Now Starts at Just $22.49
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12. We are also a leading provider of Test Prep help for Standardized Tests (SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE, and AP).
What makes eTutorWorld stand apart are: flexibility in lesson scheduling, quality of hand-picked tutors, assignment of tutors based on academic counseling and diagnostic tests of each student, and our 100% money-back guarantee.
Whether you have never tried personalized online tutoring before or are looking for better tutors and flexibility at an affordable price point, schedule a FREE TRIAL Session with us today.
*There is no purchase obligation or credit card requirement
Grade 7 Science Worksheets
- Elements and Compounds
- Solar Energy
- Photosynthesis
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Law of conservation of energy
- Periodic table
- Properties of Matter
- Waves
- Energy Resources
- Weather and Climate
- Immune, Circulatory and Digestive Systems
- Organs in Multi-cellular Organism
- Sedimentary, Igneous, and Metamorphic Rocks
- Structure of the Earth
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Scientific Method
- Human Digestive System
- Environmental Science
- Renewable and Non-renewable energy Resources
- Characteristics of Living Organisms
- Life Science
- Earth and Space Science
- Solar Eclipse
- Heat Technology
- Newton’s Laws of Motions
- Physical Science
- Tools, Measurement and SI Units
- Earth Atmosphere
- Interactions of Living things
- The Earth Ecosystem
- Organelles in Plant and Animal cells
- Layers of the Earth
- Cycles in Nature
Grade 7 Math Worksheets
- Fractions
- Linear equations word problems
- Statistics
- Properties of Parallel Line
- Finding slope from an equation
- Identifying Quadrilaterals
- Percent Change
- Properties of addition and multiplication
- Pythagorean Theorem
- Solving two step inequalities
- Symmetry
- Fractions to Decimals (New)
- Whole Number Exponents with Integer Bases (New)
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions (New)
- Integer Addition and Subtraction (New)
- Dividing Mixed Numbers (New)
- Basics of Coordinate Geometry (New)
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird










