The Circulatory System
Grade 7 Science Worksheets
The human circulatory system is a complex network of blood vessels and heart that transports blood, oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
Table of Contents:
- Characteristics of the Human Circulatory System
- Components of the Human Circulatory System
- Working of the Heart
- FAQs
The Circulatory System - Grade 7 Science Worksheet PDF
This is a free printable / downloadable PDF worksheet with practice problems and answers. You can also work on it online.
|
Untimed | |
Sign up with your email ID to access this free worksheet.
"We really love eTutorWorld!"
"We really love etutorworld!. Anand S and Pooja are excellent math teachers and are quick to respond with requests to tutor on any math topic!" - Kieran Y (via TrustSpot.io)
"My daughter gets distracted easily"
"My daughter gets distracted very easily and Ms. Medini and other teachers were patient with her and redirected her back to the courses.
With the help of Etutorworld, my daughter has been now selected in the Gifted and Talented Program for the school district"
- Nivea Sharma (via TrustSpot.io)
Characteristics of the Human Circulatory System
The human circulatory system has the following characteristics:
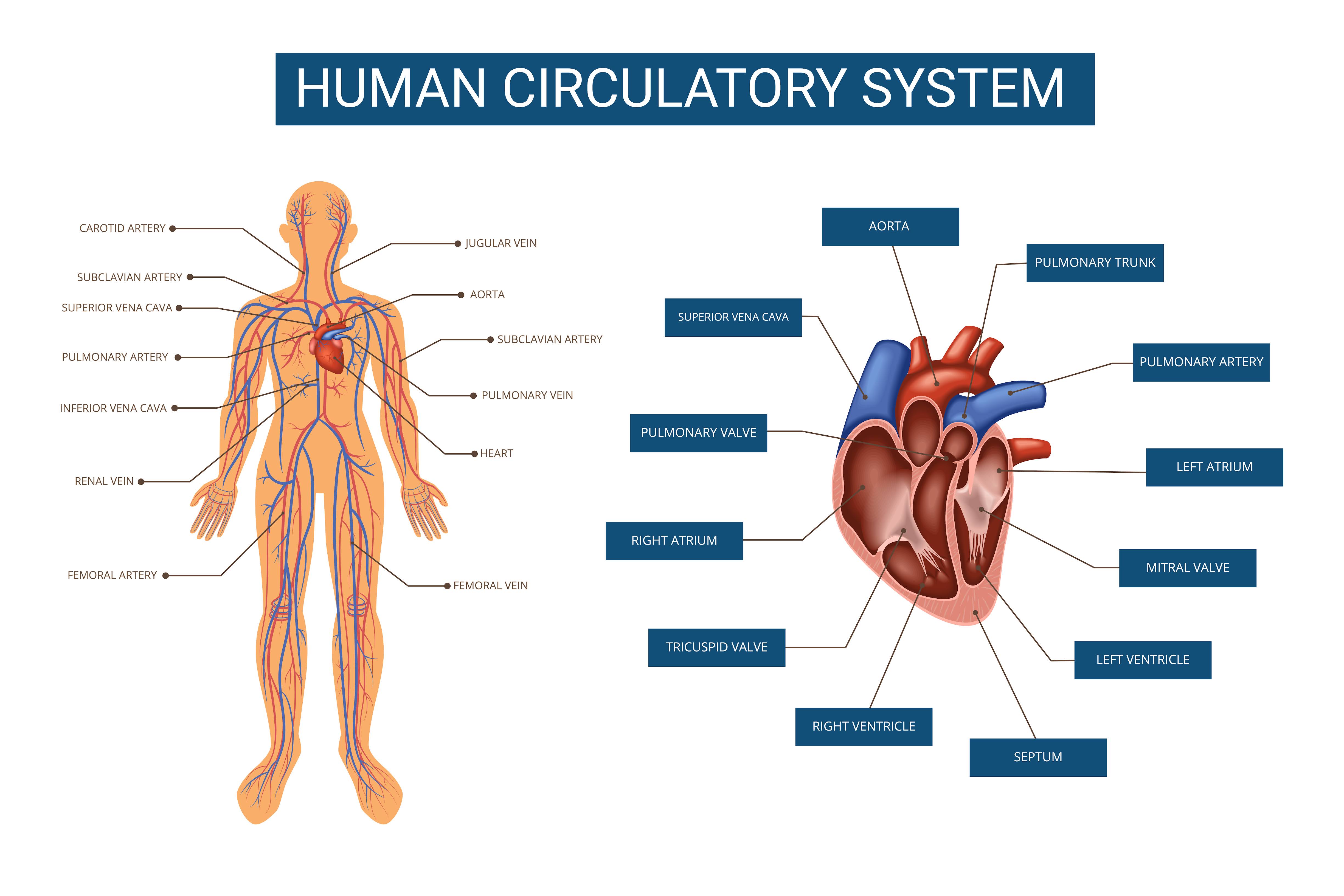
Continuous flow: The human circulatory system is designed to maintain a continuous flow of blood throughout the body. This helps to ensure that all tissues and organs receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients.
Dual circulations: The human circulatory system is divided into two circulations: the pulmonary circulation, which delivers blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the systemic circulation, which delivers oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
Heart-centered design: The human circulatory system is designed around the heart, which is the center of the circulatory system and the primary pump that moves blood throughout the body. The heart and the circulatory system make up the human cardiovascular system.
Blood vessels: The human circulatory system is composed of a network of blood vessels, including arteries, capillaries, and veins, that transport blood to and from the heart.
Blood composition: Blood is a vital fluid that is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Each component of blood plays a unique role in the circulatory system, from carrying oxygen and nutrients to protecting against infections and injuries.
Regulation of blood pressure: The human circulatory system is designed to regulate blood pressure, which helps to ensure that blood flows at a consistent rate to all parts of the body.
Adaptability: The human circulatory system is adaptable, responding to changes in physical activity, temperature, and other environmental factors to maintain optimal blood flow and deliver the right balance of oxygen and nutrients to cells.
Components of the Human Circulatory System
The human circulatory system consists of the following components:
Heart: The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest that pumps blood throughout the body. It has four chambers: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
Blood vessels: Blood vessels are tubes that carry blood throughout the body. They are divided into three types: arteries, capillaries, and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart and have thick walls to withstand the pressure generated by the heartbeat. Capillaries are small blood vessels that allow for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and body tissues. Veins return blood to the heart and have thinner walls than arteries.
Blood: Blood is a vital fluid that transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body. Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Blood plasma: Blood plasma is a yellowish fluid that makes up about 55% of total blood volume. It carries nutrients, hormones, waste products, and other substances throughout the body.
Red blood cells: Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, carry oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues. They have a biconcave shape and contain the protein hemoglobin, which binds to oxygen.
White blood cells: White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are involved in the body’s immune response. They help to fight infections and remove foreign substances from the body.
Platelets: Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, play a crucial role in blood clotting. They help to prevent bleeding by forming clots at sites of injury.
“There have been times when we booked them last minute, but the teachers have been extremely well-prepared and the help desk at etutorworld is very prompt.
Our kid is doing much better with a higher score.”
7th Grade Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers Personalized Online Tutoring for Math, Science, English, and Standardised Tests.
Our Tutoring Packs start at just under $21 per hour, and come with a moneyback guarantee.
Schedule a FREE Trial Session, and experience quality tutoring for yourself. (No credit card required.)
Working of the Heart
The heart is an organ in your chest that pumps blood throughout your body. It’s a muscle that works really hard to keep you alive!
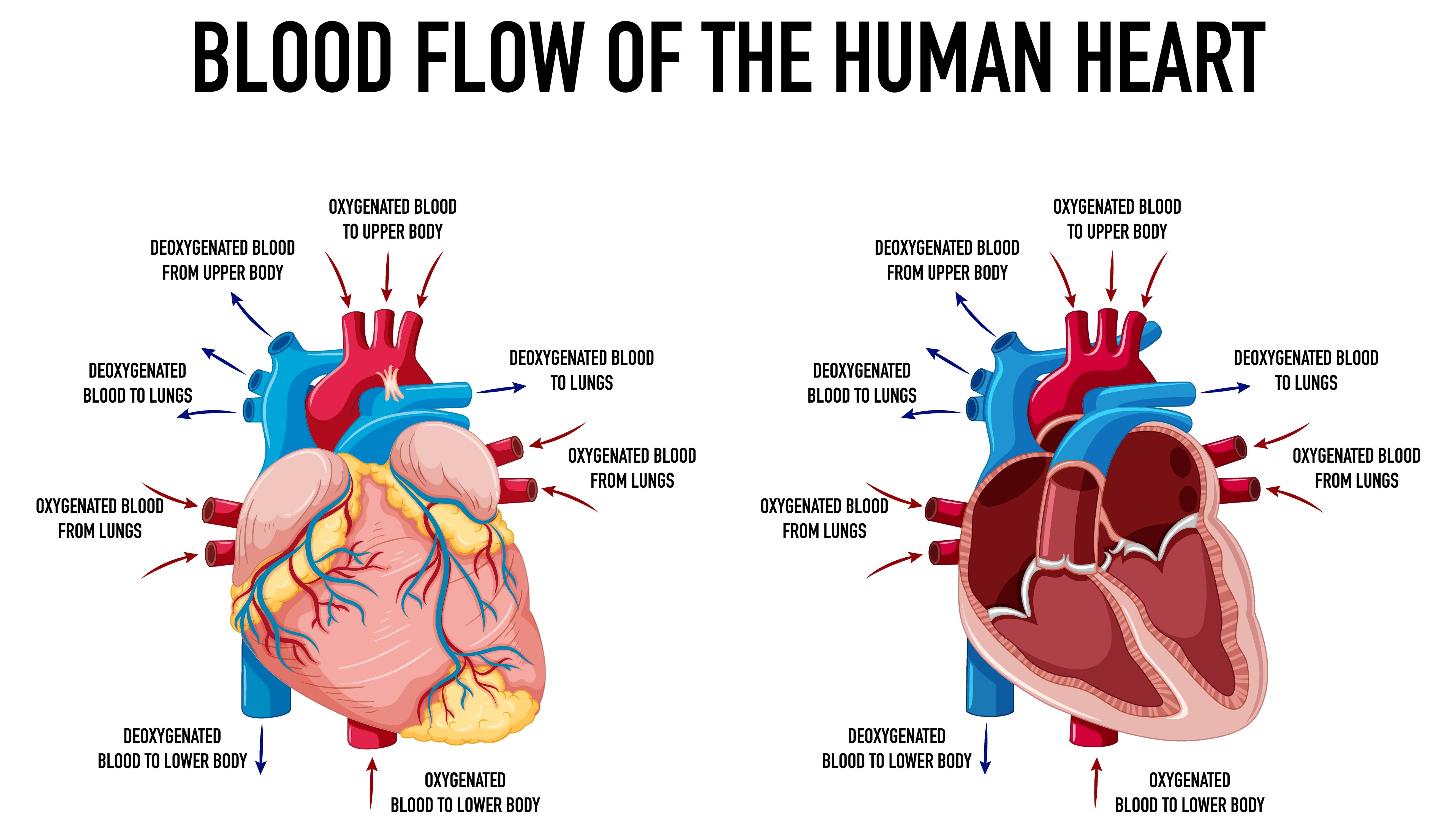
The heart has four chambers: the right atrium, the right ventricle, the left atrium, and the left ventricle. These chambers are separated by valves that make sure blood flows in the right direction.
When you breathe in, your body gets oxygen from the air. This oxygen-rich air goes into your lungs and enters your bloodstream. The blood then travels to the heart and enters the left atrium. From there, it goes into the left ventricle.
When the right ventricle contracts, it pumps the oxygen-poor blood out of the heart and into your lungs. This blood picks up more oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide, a waste product from your body. The oxygen-rich blood then goes back into the heart, entering the left atrium.
From the left atrium, the blood travels into the left ventricle. The left ventricle is the strongest chamber of the heart and it pumps the oxygen-rich blood out of the heart and into the rest of the body.
This process happens over and over again, with the heart contracting and relaxing to pump blood throughout the body. It’s important to keep your heart healthy by eating well, exercising, and avoiding things like smoking and too much junk food.
Do You Stack Up Against the Best?
If you have 30 minutes, try our free diagnostics test and assess your skills.
The Circulatory System FAQS
What is the function of the human circulatory system?
The human circulatory system is responsible for delivering oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products to and from the body’s tissues. It also helps regulate blood pressure and maintains the body’s fluid balance.
How does the heart work in the human circulatory system?
The heart works as a pump that drives the flow of blood throughout the body. It contracts and relaxes in a rhythmic fashion, driving blood from the atria to the ventricles and then out to the body’s tissues through the arterial system.
What are the main types of blood vessels in the human circulatory system?
The main types of blood vessels in the human circulatory system are arteries, capillaries, and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart, capillaries allow for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and body tissues, and veins return blood to the heart.
What is blood and what are its components?
Blood is a vital fluid that transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body. Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What is the role of hemoglobin in the human circulatory system?
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that binds to oxygen. It plays a crucial role in the human circulatory system by transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues.
What is the function of white blood cells in the human circulatory system?
White blood cells are involved in the body’s immune response. They help to fight infections and remove foreign substances from the body.
What is the role of platelets in the human circulatory system?
Platelets play a crucial role in blood clotting. They help to prevent bleeding by forming clots at sites of injury.

Kathleen Currence is one of the founders of eTutorWorld. Previously a middle school principal in Kansas City School District, she has an MA in Education from the University of Dayton, Ohio. She is a prolific writer, and likes to explain Science topics in student-friendly language. LinkedIn Profile
Affordable Tutoring Now Starts at Just $22.49
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12. We are also a leading provider of Test Prep help for Standardized Tests (SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE, and AP).
What makes eTutorWorld stand apart are: flexibility in lesson scheduling, quality of hand-picked tutors, assignment of tutors based on academic counseling and diagnostic tests of each student, and our 100% money-back guarantee.
Whether you have never tried personalized online tutoring before or are looking for better tutors and flexibility at an affordable price point, schedule a FREE TRIAL Session with us today.
*There is no purchase obligation or credit card requirement
Grade 7 Science Worksheets
- Elements and Compounds
- Solar Energy
- Photosynthesis
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Law of conservation of energy
- Periodic table
- Properties of Matter
- Waves
- Energy Resources
- Weather and Climate
- Immune, Circulatory and Digestive Systems
- Organs in Multi-cellular Organism
- Sedimentary, Igneous, and Metamorphic Rocks
- Structure of the Earth
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Scientific Method
- Human Digestive System
- Environmental Science
- Renewable and Non-renewable energy Resources
- Characteristics of Living Organisms
- Life Science
- Earth and Space Science
- Solar Eclipse
- Heat Technology
- Newton’s Laws of Motions
- Physical Science
- Tools, Measurement and SI Units
- Earth Atmosphere
- Interactions of Living things
- The Earth Ecosystem
- Organelles in Plant and Animal cells
- Layers of the Earth
- Cycles in Nature
Grade 7 Math Worksheets
- Fractions
- Linear equations word problems
- Statistics
- Properties of Parallel Line
- Finding slope from an equation
- Identifying Quadrilaterals
- Percent Change
- Properties of addition and multiplication
- Pythagorean Theorem
- Solving two step inequalities
- Symmetry
- Fractions to Decimals (New)
- Whole Number Exponents with Integer Bases (New)
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions (New)
- Integer Addition and Subtraction (New)
- Dividing Mixed Numbers (New)
- Basics of Coordinate Geometry (New)
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird










