Chemical Properties of Matter Worksheets
Grade 8 Science Worksheets
Chemical properties of matter refer to the characteristics and behaviors of substances that can be observed during chemical reactions or interactions with other substances.
Learn and reinforce your learning with free chemical properties of matter worksheets.
Introduction | Chemical Properties of Matter Worksheets
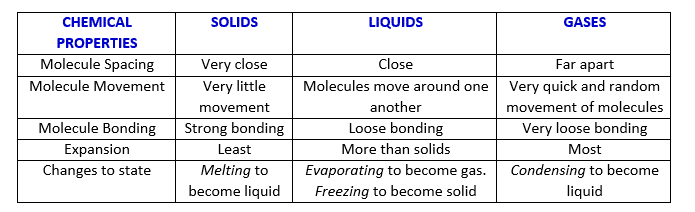
The states of matter have chemical properties that distinguish them from one another. Some of the physical properties are tabulated below:
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
The Periodic Table
All known naturally occurring elements in the Universe, and some artificially created ones, are represented in a standard format known as the Periodic Table. Elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic number (the number of protons in the nucleus). The rows of the table are known as periods and the columns are known as groups. The elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number from left to right and from top to bottom.
Other periodic trends are also observed in the arrangement of the table, the atom size, for example, which is measured by the atomic radius of the atom.
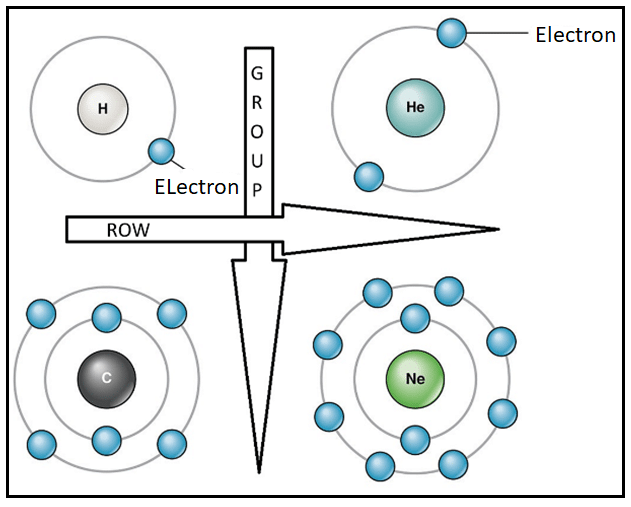
As the atomic number increases along any row of the periodic table, the additional electrons associated with this increase are packed into the same orbit or energy level of the atom. At this same energy orbit, the increased nuclear charge (due to addition of the proton) attracts the orbiting electrons much more strongly, making the size of the atom smaller along the row.
As one moves down the periodic table, i.e. down a column or group, the atomic radius increases due to an increase in the orbits of electrons. The atom is, therefore, larger in size as you move down the table.
Some columns or groups have been given special names based on the chemical properties of the elements in that column. Halogens for example are highly chemically reactive while Noble Gases have very low chemical reactivity.
CHEMICAL BONDING
One of the chemical properties of matter is that their atoms have a tendency to bond with other atoms. All atoms have electrons revolving around their nuclei in defined energy levels called orbits. The electrons in the outermost orbit are known as valence electrons. In any chemical reaction, these valence electrons are gained or lost between atoms, creating chemical bonds between the atoms.
Atoms of the same element may combine to form Molecules. For example, two oxygen atoms combine to form an oxygen molecule. Atoms of two different elements may also combine to form a molecule. For example, two atoms of hydrogen combine with one atom of oxygen to form a molecule named water. When atoms of different elements combine, the result is named a Compound. Water is thus a compound as well. So, all compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds!
Chemical bonds may be formed or destroyed as a result of a chemical reaction. Breaking bonds require energy while forming new bonds to release energy.
TYPES OF CHEMICAL BONDS
A chemical bond that involves a sharing of valence electrons (not an exchange of electrons) between two or more atoms is termed a Covalent Bond. This typically takes place between two non-metals, such as when two hydrogen atoms combine to form a hydrogen molecule, or when carbon combines with four hydrogen atoms to form methane gas.
A chemical bond that involves an exchange of valence electrons from one atom to another is termed an Ionic Bond. This typically takes place between a nonmetal and a metal. An example of an ionic bond is the combining of one atom of Sodium with one of Chlorine to create Sodium Chloride, which is a common salt.
A chemical bond that takes place between two metals is termed a Metallic Bond. The valence electrons are not just associated with a specific pair of atoms here, instead, they continuously overlap across a large number of neighboring atoms. Examples are gold, silver, iron, aluminum, to name a few.
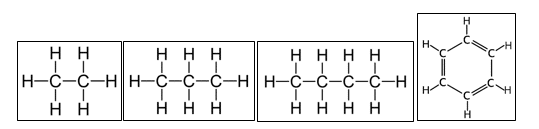
Some hydrocarbon examples (L-R: Ethane, Propane, Butane, Benzene)
Organic compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms are termed as Hydrocarbons. Multiple atoms of hydrogen and carbon combine in many different ways to create multiple types of hydrocarbons. In the examples shown, notice that in all the compounds Carbon has four covalent bonds around it while hydrogen has one. This means that they have a valency of 4 and 1 respectively!
Our energy sources such as crude oil, natural gas, coal and petroleum, are all hydrocarbons.
Check Point
State True or False:
- The molecular spacing in gas is very close.
- The periodic table is arranged by groups and rows.
- Atomic size increases as you move down the periodic table.
Fill in the Blanks:
- Electrons responsible for chemical bonding are called _____ electrons.
- A chemical bond between a metal and a nonmetal is termed an _____ bond.
- The two elements that make up hydrocarbons are _____ and _____.
Answer Key
- Gas molecules are far apart.
- True
- True
- Valence
- Ionic
- Hydrogen and Carbon
What are chemical properties?
Chemical properties refer to the characteristics and behavior of a substance when it undergoes a chemical change or interacts with other substances. These properties describe how a substance can react, transform, or combine with other substances.
How are chemical properties different from physical properties?
While physical properties describe the observable characteristics of a substance (such as color, density, or melting point), chemical properties focus on the substance’s behavior and reactivity during chemical reactions. Physical properties can be measured without changing the identity of the substance, whereas chemical properties involve the transformation of substances.
What are some examples of chemical properties?
Examples of chemical properties include flammability (the ability to burn), reactivity with acids or bases, oxidation potential, toxicity, stability, and ability to undergo specific chemical reactions. These properties provide insight into how a substance will interact with other substances under specific conditions.
Can chemical properties change?
Yes, chemical properties can change when a substance undergoes a chemical reaction or transformation. For example, a substance may change its flammability, reactivity, or toxicity when exposed to certain conditions or when reacting with other substances. These changes in chemical properties often result in the formation of new substances with different properties.
Why are chemical properties important?
Chemical properties are crucial for understanding how substances behave in different environments and how they interact with other substances. They provide valuable insights into the reactivity, stability, and potential applications or hazards of a substance. Understanding chemical properties is vital for fields such as chemistry, materials science, pharmaceuticals, and environmental science.
eTutorWorld Understands Math Tutoring | Online Math Worksheets are Important Tools
Understanding graphs, charts, and opinion polls in a newspaper, for calculating house and car payments, and for choosing a long-distance telephone service are impossible without strong math skills …and the only way to develop strong math skills is by constant practice.
‘Practice makes a man perfect’ holds true for no other field better than for math. A middle or high school student must set aside a minimum of an hour for math every day. Other than textbooks, worksheets help you revise and understand concepts better.
Our expert tutors prepare online maths worksheets that are age and grade-appropriate. Grade-wise math worksheets for Elementary Math, Arithmetic, Pre-Algebra, Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Statistics, Pre-Calculus and Calculus can be solved to improve math skills, to get ahead or to even catch up.
You may download these FREE online math worksheets in the PDF format, and then print and email us their solutions for a free evaluation and analysis by eTutorworld’smath expert tutors.
You may solve these worksheets by yourself or with your peers while studying together.
The Answer Key at the end of each worksheet allows for a self-evaluation.
Personalized Online Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12, Test Prep help for Standardized tests like SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE and AP. You may schedule online tutoring lessons at your personal scheduled times, all with a Money-Back Guarantee. The first one-on-one online tutoring lesson is always FREE, no purchase obligation, no credit card required.
For answers/solutions to any question or to learn concepts, take a FREE CLASS.
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just book a free class to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Pricing for Online Tutoring
| Tutoring Package | Validity | Grade (1-12), College |
|---|---|---|
| 5 sessions | 1 Month | $139 |
| 1 session | 1 Month | $28 |
| 10 sessions | 3 months | $269 |
| 15 sessions | 3 months | $399 |
| 20 sessions | 4 months | $499 |
| 50 sessions | 6 months | $1189 |
| 100 sessions | 12 months | $2249 |
8th Grade Free Worksheets
- The Universe
- Heredity
- Evolutionary Theory
- Structure of the atom
- Ethical Practices
- Unveiling the mystery behind the physical universe
- Components of the universe
- Celestial phenomena
- The tilt of Earth’s axis
- The causes of high and low tides
- Earth Systems
- Rocks and Fossils
- Weather and Climate
- Basics of chemical reactions
- Types of Chemical reactions – Endothermic, exothermic, oxidation, reduction reactions
- Catalysts and enzymes
- Compounds and mixtures
- Acids, Bases and pH Indicators
Images Credit:
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:206_Electron_Shells-01.jpg
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ethane-2D-flat.png
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Propane-2D-flat.png
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Butane-2D-flat.png
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Benzene_Structural_diagram.svg
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird






