Biological Evolution
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
Evolution is the gradual accumulation of small genetic variations that causes species of living organisms to change over time. The fundamental concept that underpins the study of biology and the diversity of life on Earth is evolution.
Table of Contents:
- Natural Selection
- Genetic Drift
- Evolution and Adaptation
- Differential Reproductive Success
- Mutation
- Hardy-Weinberg principle
- FAQs
Biological Evolution - Grade 6 Science Worksheet PDF
This is a free printable / downloadable PDF worksheet with practice problems and answers. You can also work on it online.
|
Untimed | |
Sign up with your email ID to access this free worksheet.
"We really love eTutorWorld!"
"We really love etutorworld!. Anand S and Pooja are excellent math teachers and are quick to respond with requests to tutor on any math topic!" - Kieran Y (via TrustSpot.io)
"My daughter gets distracted easily"
"My daughter gets distracted very easily and Ms. Medini and other teachers were patient with her and redirected her back to the courses.
With the help of Etutorworld, my daughter has been now selected in the Gifted and Talented Program for the school district"
- Nivea Sharma (via TrustSpot.io)
The theory of evolution by natural selection, proposed in the mid-nineteenth century by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, states that evolution occurs as a result of the interaction of three factors: variation, inheritance, and selection. Trait variation exists within organism populations, and some of these variations are passed down from generation to generation via inheritance.
Selection refers to the fact that some people are more likely than others to survive and reproduce and that those who are more adaptable to their surroundings are much more susceptible to passing their genes on to the next generation. This selection procedure can result in the evolution of new species over many generations.
The theory of evolution is supported by a large body of evidence from many different fields of science, such as genetics, paleontology, comparative anatomy, and biogeography. The theory of evolution is widely accepted by scientists and is regarded as one of the most well-established scientific concepts in existence.
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the process through which certain traits are becoming more or less prevalent in a population over time due to individuals with some of those traits surviving and reproducing. Individuals with better-suited traits to their ecosystem are more likely to live and reproduce, passing on those traits to their offspring. This can result in the emergence of new species over time.
Natural selection was first proposed in the mid-nineteenth century by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace. While monitoring the life diversity on the Galápagos Islands and elsewhere, Darwin and Wallace completely separately developed the concept.
The evolution of the beaks of Darwin’s finches, a group of closely connected bird species found on the Galápagos Islands, is an example of natural selection. Different finch species evolved different-looking beaks that are modified to various food sources over time.
Some species, for example, have long, thin beaks for eating bugs, while others have short, thick beaks for busting nuts. Natural selection has resulted in these differences in beak shape: finches only with the best-suited beaks for their food sources are more likely to live and reproduce, passing on their favorable characteristics to their offspring.
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is an evolutionary mechanism characterized by random fluctuations in the number of alleles (gene versions) in a group over time. Unlike natural selection, which is based on the theory that only certain traits provide a survival benefit, genetic drift is the result of chance events that cause changes in a population’s genetic makeup.
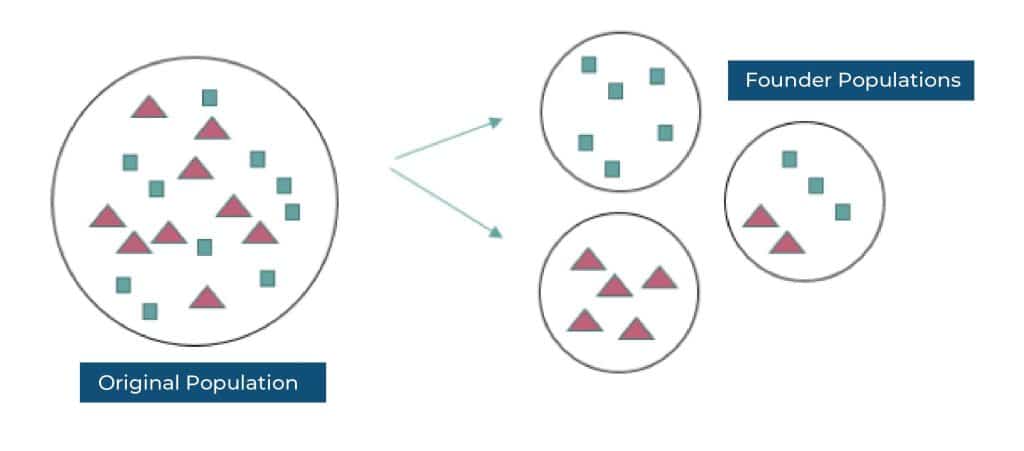
Because unpredictable events such as mutation, migration, and genetic drift can have a disproportionate effect in small populations, genetic drift can have a considerable influence on the frequency of alleles. For example, if an inhabitant of only a few individual people is separated from the rest of its own species, possible events can cause the population to lose certain alleles over time.
The founder effect, which occurs whenever a small number of people becomes secluded from such a greater population and creates a new population elsewhere, is yet another example of genetic drift. Due to the random loss of certain alleles during the founding process, the genetic makeup of the new population will differ from that of the original population.
In general, genetic drift is more prominent in tiny populations and becomes less pronounced as population size increases. The effects of genetic drift in large populations are frequently outweighed by the effects of natural selection, which could also lead to something like the evolution of new species over time.
Evolution and Adaptation
In biology, evolution and adaptation are concepts that are related. The procedure by which species of living organisms evolve over time because of the gradual accumulation of small genetic variations is referred to as evolution. The process through which a species becomes best suited to its surroundings through the formation of variations in its traits over time is referred to as adaptation.
Evolution produces adaptation. Natural selection causes organisms to become better adapted to their environment as they evolve. People with traits that really are best suited to their environment are favored by natural selection, and all these characteristics are more likely to be passed down to the next generation. This results in the emergence of new lifeforms that are better adapted to their surroundings over time.
Adaptation can be seen in a wide range of species, from chameleon camouflage to cacti’s ability to store water in their leaves. Physical adaptations, such as changes in anatomy or physiology, and behavioral adaptations, such as changes in behavior or habits, are two examples of adaptations.
Differential Reproductive Success
Differential reproductive success refers to individuals’ unequal success in reproducing and having to pass on their genes to the next generation. As the driving force behind species evolution, this idea is a crucial component of the natural selection theory of evolution. selection.
Differential reproductive success occurs when some individuals in a population outperform others in terms of reproduction. This can be due to a number of factors, such as physical characteristics, behavior, or environmental conditions. Individuals with a physical trait that allows them to better escape predators or find food, for example, are more likely to survive and breed than individuals without that trait.
As a result, that individual’s characteristics are more likely to be passed down to the next generation, and the prevalence of those characteristics in the population will rise over time.
Differential reproductive success leads to species evolution over time in this way. As individuals with advantageous traits become more prevalent in a population, the population evolves and becomes more adapted to its surroundings. Natural selection is responsible for the diversity of life on Earth, as well as the phenomenal adaptations that species have developed over time to thrive and survive in their environments.
Mutation
Genetic mutations are changes to an organism’s genome’s DNA sequence. Mutations can occur naturally as a result of DNA replication errors or as a result of exposure to environmental factors such as radiation or chemicals.
Mutations can have a wide range of effects on an organism, ranging from completely harmless and having no effect to being harmful and potentially fatal. Some mutations can result in the development of new traits or abilities that give a survival advantage, whereas others can result in genetic disorders.
Mutations play an important role in the evolution process. Mutations provide the raw material for natural selection to act on by introducing new genetic variation into a population.
Beneficial mutations that provide a survival advantage will become more common in a population over time because those individuals are more likely to survive and reproduce. Natural selection results in the evolution of new species and the development of new adaptations.
Genetic mutations are a source of genetic variation that plays an important role in the evolution process by providing raw material for natural selection to act on. While some mutations can be harmful, others can be advantageous, resulting in the evolution of new species and adaptations over time.
“There have been times when we booked them last minute, but the teachers have been extremely well-prepared and the help desk at etutorworld is very prompt.
Our kid is doing much better with a higher score.”
6th Grade Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers Personalized Online Tutoring for Math, Science, English, and Standardised Tests.
Our Tutoring Packs start at just under $22.49 per hour, and come with a moneyback guarantee.
Schedule a FREE Trial Session, and experience quality tutoring for yourself. (No credit card required.)
Convergent Evolution
This is when two different species evolve similar traits independently of each other, usually because they live in similar environments and face similar selective pressures. For example, both sharks and dolphins have evolved streamlined bodies and fins for efficient swimming, even though they are not closely related, and evolved these traits separately.
Divergent Evolution
This is when a single species evolves into multiple distinct species over time, usually because different populations become isolated from each other and adapt to different environments. For example, Darwin’s finches on the Galapagos Islands evolved different beak shapes and sizes depending on the types of food available on each island.
Adaptive Radiation
This is when a single ancestral species rapidly evolves into many different species, often because they move into new and diverse environments with many unoccupied ecological niches. For example, the cichlid fish of Lake Victoria in Africa evolved into hundreds of different species with different feeding habits and body shapes, allowing them to exploit different parts of the lake ecosystem.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
This is a mathematical model that describes how genetic variation is maintained in a population over time, assuming certain conditions are met (such as no mutation, no migration, random mating, no selection, and a large population size). Essentially, it predicts that the frequencies of different alleles (versions of a gene) will remain constant from generation to generation if these conditions are met. For example, if a population of snails has two alleles for shell color (brown and green) and the frequency of the brown allele is 0.6, then the frequency of the green allele should be 0.4 if the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Do You Stack Up Against the Best?
If you have 30 minutes, try our free diagnostics test and assess your skills.
Biological Evolution FAQs
What is the proof for evolution?
The fossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, and molecular biology are all sources of evidence for evolution.
What is the process of natural selection?
Natural selection favours individuals with characteristics that are best suited to their environment. Individuals with these traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, so they become more common in a population over time.
What exactly is the distinction between evolution and adaptation?
Evolution is the process by which living organisms’ species change over time, whereas adaptation is the process by which a species becomes more suited to its environment through the accumulation of changes in its traits over time.
What exactly is genetic drift?
Genetic drift is an evolutionary mechanism characterized by random changes in the frequency of a population’s alleles over time. It is not founded on the principle that certain characteristics provide a survival advantage, as natural selection is.
Can evolution happen quickly?
Yes, in certain conditions, including such rapid changes in the environment or the introduction of a fresh selective pressure, evolution can occur quickly. In most cases, however, evolution occurs progressively over many generations.
What role does genetic mutation play in evolution?
Genetic mutations are important in evolution because they provide raw material for natural selection to act on. Genetic mutations that offer a survival advantage become more common in a population over time.
Is evolution a violation of thermodynamic laws?
No, evolution does not violate thermodynamic laws. Evolution is a biological process that is fueled by mutations, selection, and genetic drift. The laws of thermodynamics are physical laws that govern how matter behaves.

Kathleen Currence is one of the founders of eTutorWorld. Previously a middle school principal in Kansas City School District, she has an MA in Education from the University of Dayton, Ohio. She is a prolific writer, and likes to explain Science topics in student-friendly language. LinkedIn Profile
Affordable Tutoring Now Starts at Just $22.49
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12. We are also a leading provider of Test Prep help for Standardized Tests (SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE, and AP).
What makes eTutorWorld stand apart are: flexibility in lesson scheduling, quality of hand-picked tutors, assignment of tutors based on academic counseling and diagnostic tests of each student, and our 100% money-back guarantee.
Whether you have never tried personalized online tutoring before or are looking for better tutors and flexibility at an affordable price point, schedule a FREE TRIAL Session with us today.
*There is no purchase obligation or credit card requirement
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Adaptation
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Evolution
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Astronomy
- Ecology
- Energy
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Sound
- Light
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
CogAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird










