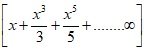Exponential and Logarithmic Series
Have you ever noticed the use of the word exponential in our daily life?
- It is used to express something which is rising or increasing at a steady and a usual rapid rate or something which increases quickly by large amounts.
Examples:
(i) Prices have increased exponentially i.e. at an exponential rate.
(ii) The budget is increasing at an exponential rate.
(iii) We all want to progress exponentially and achieve success in our lives.
- Something is said to increase or decrease exponentially if its rate of change must be expressed using exponents.
- A graph of such a rate would appear not as a straight line, but as a curve that continually becomes steeper or shallower.
- In Math, it refers to a Mathematical (function, curve, series, or equation) containing, or involving one or more numbers or quantities raised to an exponent.
So, here we try to identify what does Exponential series mean in mathematics.
Sequence
A sequence is a list or arrangement of numbers in a definite order written according to some rule or pattern.
Series
If the n terms of the sequence are a1, a2, a3, a4, ……., an then the expression a1 + a2 + a3 + a4 + ……. + an is called the series associated with the given sequence.
Exponential Series
1. A series of the form
is called the Exponential series, x ∈ R. Here ex is called the exponential function.
Replace x by –x in the above series given by (1), we obtain
= 1 +
∞ =
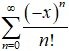
2. = 1 –
∞ =
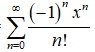
On adding (1) and (2) we have
+
= 2
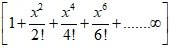
3. = 1 +
∞
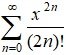
Subtracting (2) from (1),
= 2
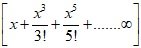
4. = x +
∞ =
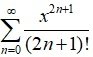
Particular cases:
Put x = 1 in (1) and (2), we have
5. ∞ =
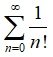
Here e is an irrational number such that 2 < e < 3.
The value of e = 2.7182818284
6. ∞ =
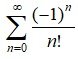
Put x = 1 in (3) and (4) we have
7. ∞ =
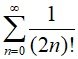
8. ∞ =
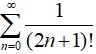
Logarithmic Series
- The logarithmic series is defined for |x| < 1 and is given by
(1+x) = x –
∞
Replace x by –x in the above series, we obtain
(1 – x) = – x –
∞ or
–(1-x) = x +
∞
On adding (1) and (2) we have
(1+x) +
(1-x) =
(1-
) = -2
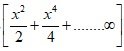 , |x|< 1
, |x|< 1
Subtracting (2) from (1), we have
(1+x)-
(1-x) =
= 2

Put x = 1 in (1), we have
2=1 –
∞ =
∞
Note: loge(1 + x) is defined for x = 1.
Examples
Now let’s consider some examples on exponential and logarithmic series.
Example 1: Find the value of 1+ ∞ .
Since, = 1 +
∞.
Hence, put x = 5 in above expression, we have
= 1 +
∞
Example 2: Find the value of 1 – ∞
Since, = 1 –
∞
Hence, put x = 2.5 in above expression, we have
=
= 1 –
∞
Example 3: Find the value of ∞ .
∞ =
∞
=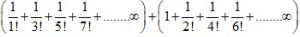
=+
=e
Example 4: Find the value of (0.5) – +
–
+……….∞
Since, (1+x) = x –
∞
Hence, put x = 0.5 we have
(1+0.5) = (0.5) –
∞
log = log
= (0.5) –
∞
Example 5: Find the value of .∞.
Since, (1-x) = -x –
∞
–(1-x) = x +
∞
Hence, put x= we have

Check Point
- Find the value of
∞
- Find the value of
∞
- Find the value of
∞
- Find the value of
∞
- Find the value of
∞
Answer Key
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.
Online test prep and practice
SCAT
CogAT
SSAT
ISEE
PSAT
SAT
ACT
AP Exam
Science Tutoring
Physics Tutoring
Chemistry Tutoring
Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring
Pre-Algebra Tutoring
Algebra Tutoring
Pre Calculus Tutoring
Calculus Tutoring
Geometry Tutoring
Trigonometry Tutoring
Statistics Tutoring
Quick links
Free Worksheets
Fact sheet
Sales Partner Opportunities
Parents
Passive Fundraising
Virtual Fundraising
Our Expert Tutors
Safe and Secure Tutoring
Interactive Online Tutoring
After School Tutoring
Elementary School Tutoring
Middle School Tutoring
High School Tutoring
Home Work Help
Math Tutors New York City
Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld
Terms of use
Privacy Policy
Site by Little Red Bird